3次元空間の描画について考えてみる
2次元からやっほ~、ポテトちゃんだよぉ((((((
今回は3次元の情報をどうやって平面上に映しだすかという話をします
ちなみに、3Dライブラリがどう作られてるかとか実際どういう理論で動いてるかとか知りません
まずは考え方です
これで大体話は終わりなんですよね←
視界が奥に行くにつれて広くなる感じを考えてみてください
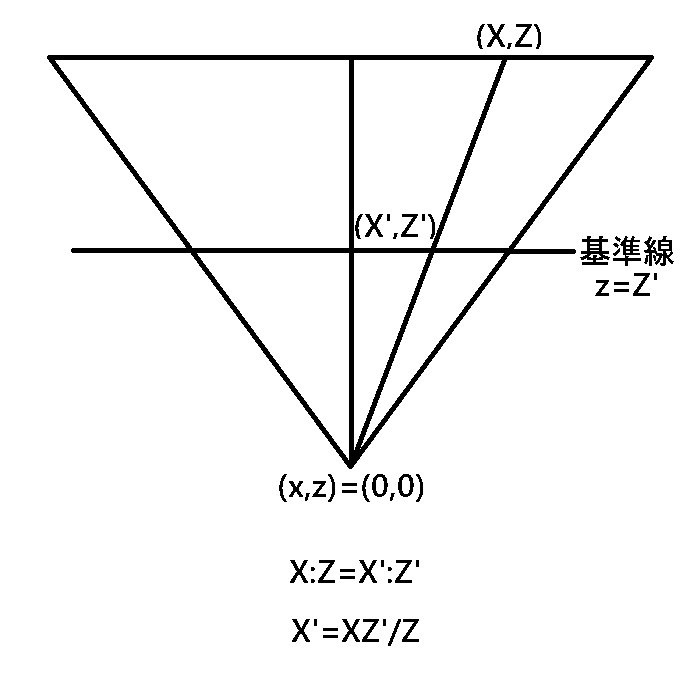
xyz座標でzを奥行きとして、z=Z'の平面に映る像を見ているとします
あくまで見ているのはその平面上の光です、その奥を直接見ているわけではありません
光は直線で飛んでくるので、図の座標(X,Z)は基準の平面上では(X',Z')の位置に見えるはずです
図から相似の考え方でX'は求められます
ということで、これを使ってPrcessingで線を使用して3次元の情報を表示してみます
float x=0,y=0,z=200;
float xyAngle=0,yzAngle=0,zxAngle=0;
float edges[][][]={
{{50,50,50},{50,50,-50}},
{{50,50,50},{-50,50,50}},
{{-50,50,-50},{50,50,-50}},
{{-50,50,50},{-50,50,-50}},
{{50,50,50},{50,-50,50}},
{{50,50,-50},{50,-50,-50}},
{{-50,50,50},{-50,-50,50}},
{{-50,50,-50},{-50,-50,-50}},
{{50,-50,50},{50,-50,-50}},
{{50,-50,50},{-50,-50,50}},
{{-50,-50,-50},{50,-50,-50}},
{{-50,-50,50},{-50,-50,-50}},
};
void setup(){
size(600,600);
textSize(20);
}
float timer=0;
void draw(){
background(255);
fill(0);
text("move key:wasd space shift\nrotate key:qer",10,20);
translate(300,300);
for(int i=0;i<edges.length;i++){
float from[]=rotateXY(rotateYZ(rotateZX(edges[i][0],zxAngle),yzAngle),xyAngle);
float to[]=rotateXY(rotateYZ(rotateZX(edges[i][1],zxAngle),yzAngle),xyAngle);
from[0]+=x;
from[1]+=y;
from[2]+=z;
to[0]+=x;
to[1]+=y;
to[2]+=z;
line(from[0]*600/from[2],-from[1]*600/from[2],to[0]*600/to[2],-to[1]*600/to[2]);
}
if(key=='r')xyAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='q')yzAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='e')zxAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='w')z++;
if(key=='a')x--;
if(key=='s')z--;
if(key=='d')x++;
if(key==' ')y++;
if(keyCode==SHIFT)y--;
}
float[] rotateXY(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0]*cos(angle)-position[1]*sin(angle);
rotated[1]=position[0]*sin(angle)+position[1]*cos(angle);
rotated[2]=position[2];
return rotated;
}
float[] rotateYZ(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0];
rotated[1]=position[1]*cos(angle)-position[2]*sin(angle);
rotated[2]=position[1]*sin(angle)+position[2]*cos(angle);
return rotated;
}
float[] rotateZX(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0]*cos(angle)-position[2]*sin(angle);
rotated[1]=position[1];
rotated[2]=position[0]*sin(angle)+position[2]*cos(angle);
return rotated;
}
void keyReleased(){
key='\0';
keyCode=0;
}
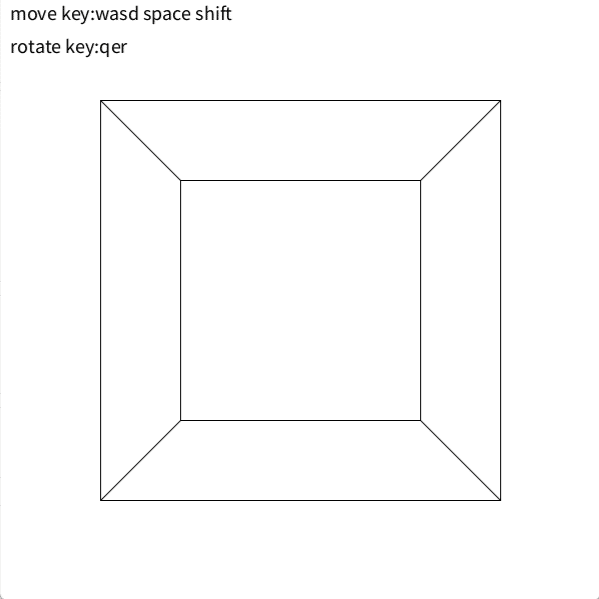
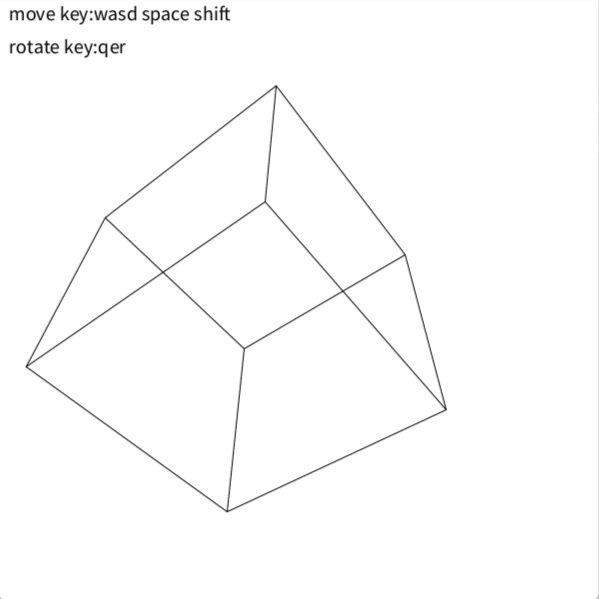
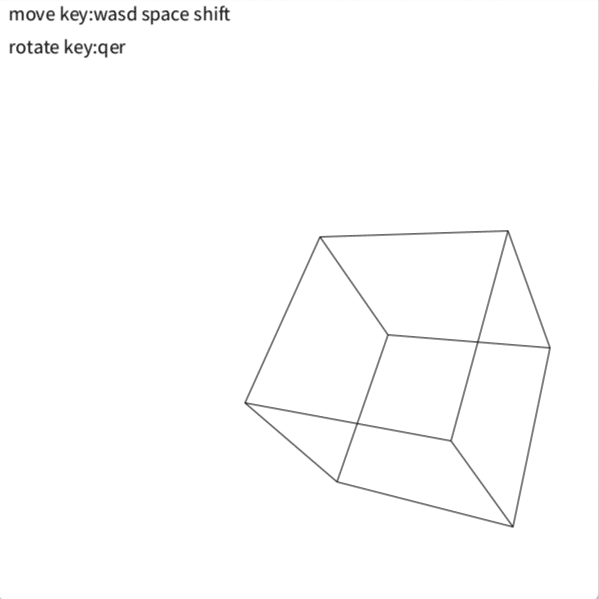
こんな感じです
edgesは各辺の両端の座標情報持ちます
rotateXX関数はその2軸間で図形を回転します、x'=xcosθ-ysinθ,y'=xsinθ+ycosθの考え方です、線形代数をやった人なら回転を表す線形変換で通じますかね(細かい話の記事はここに)
線じゃなくて平面でもやってみたんですけど
void setup(){
size(1000,600);
}
Cube cube=new Cube(0,0,200,100);
float xyAngle=0,yzAngle=0,zxAngle=0;
float timer=0;
void draw(){
background(255);
translate(500,300);
if(key=='r')xyAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='q')yzAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='e')zxAngle+=0.03;
if(key=='w')cube.z++;
if(key=='a')cube.x--;
if(key=='s')cube.z--;
if(key=='d')cube.x++;
if(key==' ')cube.y++;
if(keyCode==SHIFT)cube.y--;
cube.rotate(xyAngle,yzAngle,zxAngle);
cube.show();
}
class Cube{
float surfaces[][][]={
{{0.5,0.5,0.5},{0.5,0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,0.5,0.5}},
{{0.5,-0.5,0.5},{0.5,-0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,0.5}},
{{0.5,0.5,0.5},{0.5,0.5,-0.5},{0.5,-0.5,-0.5},{0.5,-0.5,0.5}},
{{0.5,0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,-0.5},{0.5,-0.5,-0.5}},
{{-0.5,0.5,-0.5},{-0.5,0.5,0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,-0.5}},
{{0.5,0.5,0.5},{-0.5,0.5,0.5},{-0.5,-0.5,0.5},{0.5,-0.5,0.5}},
};
float rotated[][][]=new float[6][4][3];
float x,y,z;
Cube(float newx,float newy,float newz,float len){
x=newx;
y=newy;
z=newz;
for(int i=0;i<surfaces.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<surfaces[0].length;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
surfaces[i][j][k]*=len;
}
rotated[i][j][0]=surfaces[i][j][0]+x;
rotated[i][j][1]=surfaces[i][j][1]+y;
rotated[i][j][2]=surfaces[i][j][2]+z;
}
}
}
void rotate(float xyAngle,float yzAngle,float zxAngle){
for(int i=0;i<surfaces.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<surfaces[0].length;j++){
rotated[i][j]=rotateXY(rotateYZ(rotateZX(surfaces[i][j],zxAngle),yzAngle),xyAngle);
rotated[i][j][0]+=x;
rotated[i][j][1]+=y;
rotated[i][j][2]+=z;
}
}
}
void show(){
sortSurface(rotated,x,y,z);
fill(100,100,255);
strokeWeight(3);
for(int i=0;i<surfaces.length;i++){
beginShape();
for(int j=0;j<surfaces[0].length;j++){
vertex(rotated[i][j][0]*600/rotated[i][j][2],-rotated[i][j][1]*600/rotated[i][j][2]);
}
vertex(rotated[i][0][0]*600/rotated[i][0][2],-rotated[i][0][1]*600/rotated[i][0][2]);
endShape();
}
}
}
float[] rotateXY(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0]*cos(angle)-position[1]*sin(angle);
rotated[1]=position[0]*sin(angle)+position[1]*cos(angle);
rotated[2]=position[2];
return rotated;
}
float[] rotateYZ(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0];
rotated[1]=position[1]*cos(angle)-position[2]*sin(angle);
rotated[2]=position[1]*sin(angle)+position[2]*cos(angle);
return rotated;
}
float[] rotateZX(float[] position,float angle){
float rotated[]=new float[3];
rotated[0]=position[0]*cos(angle)-position[2]*sin(angle);
rotated[1]=position[1];
rotated[2]=position[0]*sin(angle)+position[2]*cos(angle);
return rotated;
}
void sortSurface(float surfaces[][][],float x,float y,float z){
float toCenter[][][]=new float[surfaces.length][surfaces[0].length][3];
float signX=1,signY=1;
if(x<0)signX*=-1;
if(y<0)signY*=-1;
float zxAngle=signX*(PI/2-atan(signX*z/x));
float yzAngle=signY*atan(signY*y/z);
for(int i=0;i<surfaces.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<surfaces[0].length;j++){
toCenter[i][j]=rotateZX(rotateYZ(surfaces[i][j],yzAngle),zxAngle);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<toCenter.length-1;i++){
int maxIndex1=i;
int maxIndex2=0;
for(int j=i;j<toCenter.length;j++){
float max=toCenter[j][0][2];
int maxIndex=0;
for(int k=0;k<toCenter[j].length;k++){
if(toCenter[j][k][2]<max)continue;
max=toCenter[j][k][2];
maxIndex=k;
}
if(max<toCenter[maxIndex1][maxIndex2][2])continue;
maxIndex1=j;
maxIndex2=maxIndex;
}
float tmp;
for(int k=0;k<toCenter[0].length;k++){
for(int l=0;l<3;l++){
tmp=toCenter[i][k][l];
toCenter[i][k][l]=toCenter[maxIndex1][k][l];
toCenter[maxIndex1][k][l]=tmp;
tmp=surfaces[i][k][l];
surfaces[i][k][l]=surfaces[maxIndex1][k][l];
surfaces[maxIndex1][k][l]=tmp;
}
}
}
}
void keyReleased(){
key='\0';
keyCode=0;
}
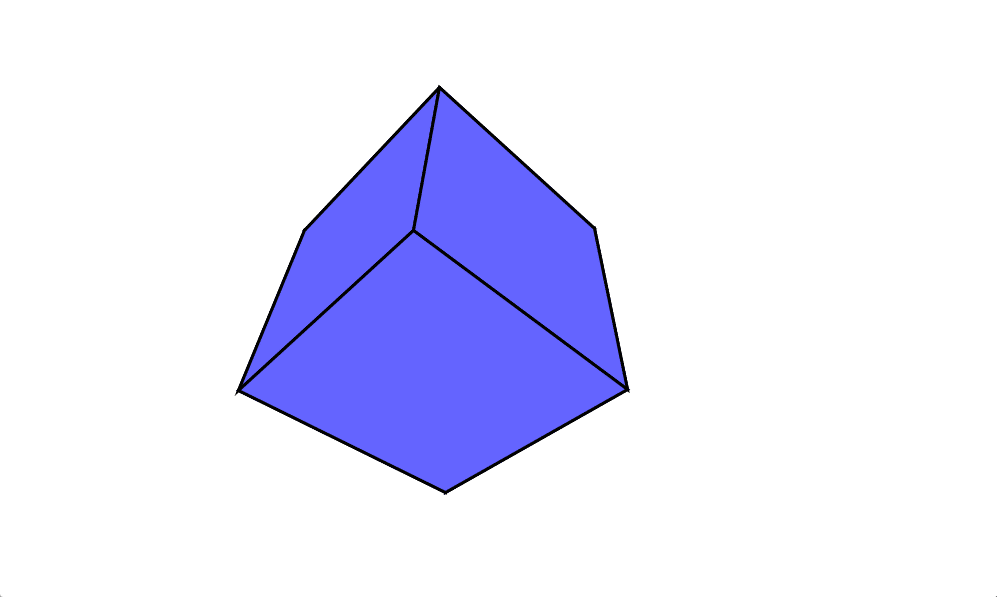
上に表示する面の選択が分からなかったので立方体限定です
物体が後ろにあるときのことは特に考えてませんが、z座標が0以下になったら表示しないようにすればいいと思います
自分が移動したときはその分物体の座標を引いて、回転したときはその分物体の座標を自分中心に逆に回せば対応できるはずです
ということで、こんな感じの話でした
それではまた~
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
