
建築・土木領域における最新のAIの活用事例(2023年6月)
近年の生成AIに代表されるように、AIの精度や活用方法は急速に広がっており、建築・土木領域でも幅広い場面での活用が期待されています。ここでは、最新の研究やサービスの事例を踏まえて、網羅的にAIの活用事例を概観したいと思います。
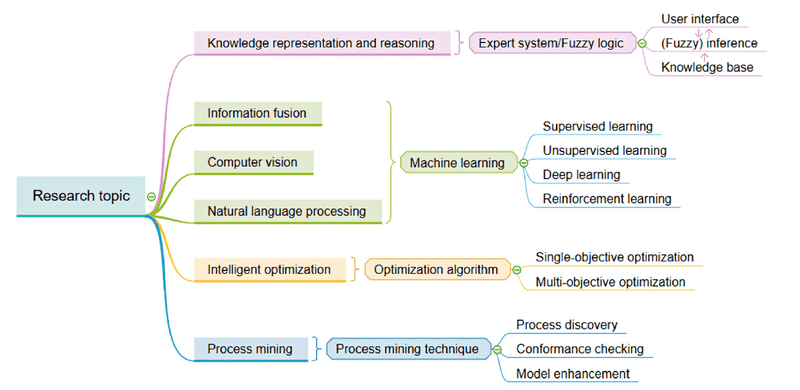
AIの種類
AIを大きく分類するとエキスパートシステム、ファジーロジック、機械学習、最適化アルゴリズムの4つのグループに大別されます (Mellit & Kalogirou, 2008)。その中でも機械学習はDeep learningや強化学習など、ChatGPTや画像生成などの生成AIでも用いられる領域で、画像認識、物体検出、音声認識、自然言語処理など様々な用とで発展が急速に進んでいます。
建築・土木領域のAIの活用事例
建築・土木領域においてどのようにAIが活用されてきたのか記載します。建築・土木領域を計画・設計プロセス、施工プロセス、運用・維持管理プロセスの3つにわけて説明します。
計画・設計プロセス
調査
不動産価格の推定(Opendoor, LoftyAI)
https://www.opendoor.com/homes
デザイン
建築設計に適用される機械学習アルゴリズム (Hong et al., 2020)
デザイン生成
GANアルゴリズムの活用(Huang & Zheng, 2018; Liu et al, 2017)
ANNアルゴリズムの活用 (Tamke et al., 2018)
屋根トラスの形状最適化(Bailey Breanna & Raich Anne M., 2012)
デザイン評価
Plain ANNアルゴリズムの活用 (Lorenz et al., 2018)
ANN、PCA、SVMアルゴリズムの活用 (Zhou & Liu, n.d.)
ランダムフォレストアルゴリズムの活用 (Y. Zhang et al., 2018)
https://www.conx.co/
構造設計
(1)構造物の応答と性能の予測、(2)実験データの解釈とコンポーネントレベルの構造特性を予測するモデルの策定、(3)画像とテキストを用いた情報検索、(4)構造ヘルスモニターデータのパターン認識(Sun et al., 2021)
BIM・CIMへの統合
AIを活用して形状モデリングや物体認識をし、レーザースキャナデータからBIMモデルを作成するプロセスを自動化(Tang et al., 2010)
プロセスマイニング
BIMログをマイニングし、デザインの生産性の改善施策を分析 (Pan & Zhang, 2020)
BIMでの設計における情報の蓄積や変化を解析する (Al Hattab & Hamzeh, 2018)
https://pillarplus.com/ai-tech/
施工プロセス
プロジェクトのスケジューリング
プロジェクトの工程の最適化によってコストの最小化する(Alavipour & Arditi, 2019)
建設現場でのモニタリング
YOLOアルゴリズムの活用(Nath et al., 2020)
保護具(PPE)の不適切な使用、危険区域の露出、転倒の危険、安全手順や計画されたワークフローに従わないことを検出する (Fang et al., 2020)
コンピュータービジョンを活用し、梁、柱、壁、スラブなどの建築物の検出 (Brilakis & Soibelman, 2008)

https://prtimes.jp/main/html/rd/p/000000018.000100410.html
自動化された建設製造
AI技術と情報通信、製造、関連製品技術との融合し、工事や製造の自動化 (Li et al., 2017)(Hatami Mohsen et al., n.d.)(Li et al., 2017)
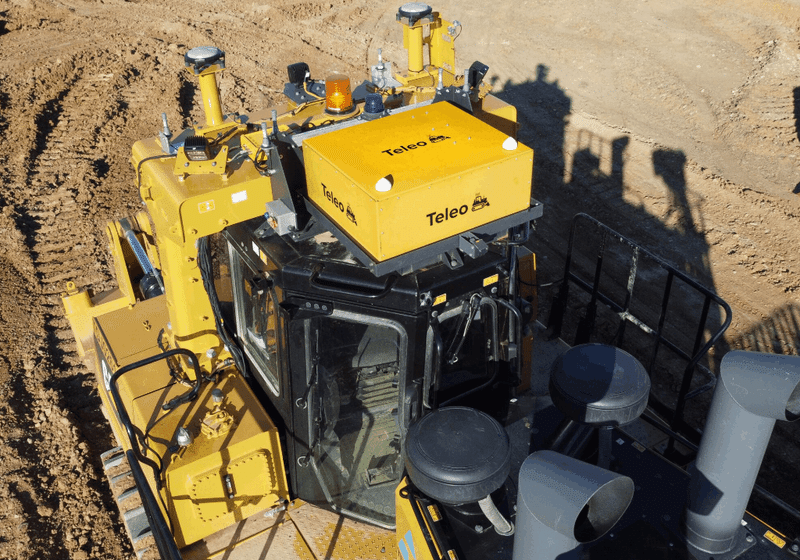

https://www.teleo.ai/technology/
構造工学
構造計算の自動化 (Salehi & Burgueño, 2018)
https://www.structure-pal.com/preplan
コスト分析
サポートベクターマシン(SVM)を用いた建設段階における物流コストの予測手法で、SVMのパラメータを調整するための反復アルゴリズムを活用 (Tian et al., 2009)
エネルギー消費量
建物のエネルギー使用量を予測(Wang & Srinivasan, 2017)(H.-X. Zhao & Magoulès, 2012)Himeur et al, 2021)
安全性
作業員の安全行動向上のために最もインパクトのある安全対策を分析(Mazlina Zaira & Hadikusumo, 2017)
鉄骨建築プロジェクトにおいて、対象物の落下・崩壊・感電のリスクを低減するため、安全リスクの確率を算出し、事故原因を検討するベイジアンネットベースの安全リスク評価を開発(Leu & Chang, 2013)
コンピュータビジョンは、建築物、橋梁、トンネル、道路、下水道管など、様々な種類の社会基盤に発生する欠陥や損傷(亀裂、剥離、腐食、穴、接合部の損傷など)を自動的に検出・評価し、構造システムの安全性と耐用性を検証
ディープラーニングとテキストマイニングを活用し、ハザードパターンや、時間の経過とともに事故の危険性の変遷を解析(Zhong et al., 2020)
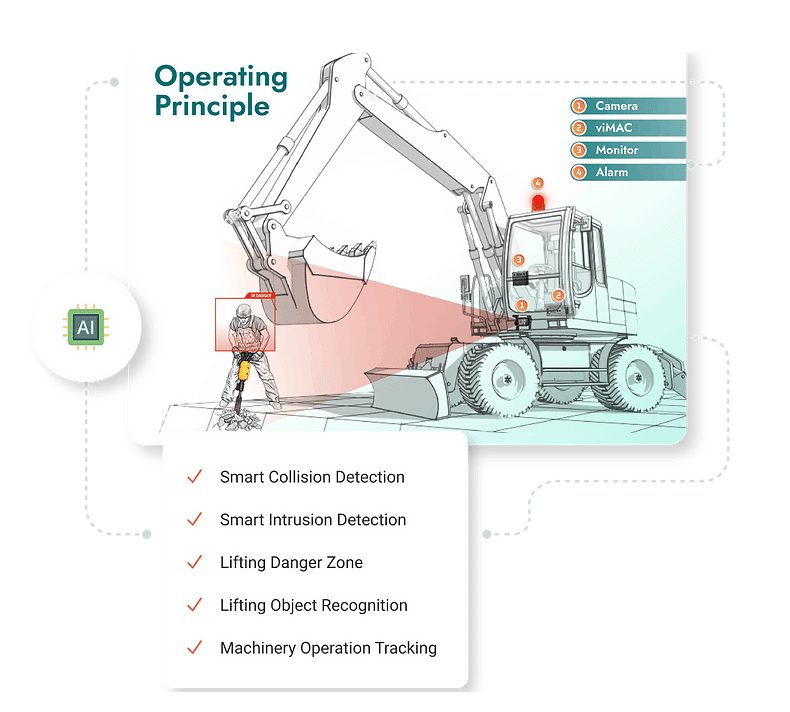
https://www.viact.ai/vimac

https://prtimes.jp/main/html/rd/p/000000021.000100410.html
建設廃棄物処理
建設・解体廃棄物を認識するためにコンピュータビジョンを適用 (Kuritcyn et al., 2015)
運用・維持管理プロセス
構造物ヘルスモニタリング
建築物、橋梁、トンネル、道路、下水道管などの各種社会基盤に発生する欠陥や損傷(亀裂、剥離、腐食、穴、接合部の損傷など)を検出・評価し、構造システムの安全性と耐用性を検証 (C. Zhang et al., 2020)

https://prtimes.jp/main/html/rd/p/000000024.000100410.html

https://www.flocksafety.com/
故障検出診断(FDD)
空調などの建物設備の故障を検出・診断(Y. Zhao et al., 2019)
HVACシステム
可変風量(VAV)の最適化 (Wu & Sun, 2011)
ビルディングレトロフィット(既存構造物への新しい設備等を導入)
Light Detection and Ranging(LiDAR)を用いて、ランダムフォレストで建物の築年数を予測(Tooke et al., 2014)
2次元の建ぺい地や高さなどの建物の形状から、建築物のタイプを予測 (Henn et al., 2012)
電力負荷予測
スマートグリッドへの活用を想定した電気負荷予測(Raza & Khosravi, 2015)
まとめ
ここでは、建築・土木領域を計画・設計プロセス、施工プロセス、運用・維持管理プロセスの3つにわけて、AIの活用事例を整理しました。今後とも、AIは急速に発展し、様々な場面で活用されることが想定されます。
ChatGPTなどの生成AIの活用についてはこちらの記事をご参照ください。
mignは建築・土木領域で先端技術を活用したソフトウェア・ハードウェアを開発しています。この記事でご紹介したソリューションの開発のご希望など、お気軽にご相談ください。
https://www.mign.io/
参考文献
aAlavipour, S. M. R., & Arditi, D. (2019). Time-cost tradeoff analysis with minimized project financing cost. Automation in Construction, 98, 110–121.
Al Hattab, M., & Hamzeh, F. (2018). Simulating the dynamics of social agents and information flows in BIM-based design. Automation in Construction, 92, 1–22.
Brilakis, I. K., & Soibelman, L. (2008). Shape-based retrieval of construction site photographs. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering. https://ascelibrary.org/doi/abs/10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(2008)22:1(14)
Fang, W., Love, P. E. D., Luo, H., & Ding, L. (2020). Computer vision for behaviour-based safety in construction: A review and future directions. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 43, 100980.
Hatami Mohsen, Flood Ian, Franz Bryan, & Zhang Xun. (n.d.). State-of-the-Art Review on the Applicability of AI Methods to Automated Construction Manufacturing. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 368–375.
Henn, A., Römer, C., Gröger, G., & Plümer, L. (2012). Automatic classification of building types in 3D city models. GeoInformatica, 16(2), 281–306.
Kuritcyn, P., Anding, K., Linß, E., & Latyev, S. M. (2015). Increasing the safety in recycling of construction and demolition waste by using supervised machine learning. Journal of Physics. Conference Series, 588, 012035.
Leu, S.-S., & Chang, C.-M. (2013). Bayesian-network-based safety risk assessment for steel construction projects. Accident; Analysis and Prevention, 54, 122–133.
Li, B.-H., Hou, B.-C., Yu, W.-T., Lu, X.-B., & Yang, C.-W. (2017). Applications of artificial intelligence in intelligent manufacturing: a review. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 18(1), 86–96.
Lorenz, C.-L., Packianather, M., Spaeth, A., & Bleil De Souza, C. (2018). Artificial neural network-based modelling for daylight evaluations. SimAUD 2018, Delft, The Netherlands. https://orca.cardiff.ac.uk/id/eprint/112040/
Mazlina Zaira, M., & Hadikusumo, B. H. W. (2017). Structural equation model of integrated safety intervention practices affecting the safety behaviour of workers in the construction industry. Safety Science, 98, 124–135.
Mellit, A., & Kalogirou, S. A. (2008). Artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic applications: A review. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34(5), 574–632.
Nath, N. D., Behzadan, A. H., & Paal, S. G. (2020). Deep learning for site safety: Real-time detection of personal protective equipment. Automation in Construction, 112, 103085.
Pan, Y., & Zhang, L. (2020). BIM log mining: Exploring design productivity characteristics. Automation in Construction, 109, 102997.
Pan, Y., & Zhang, L. (2021). Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Automation in Construction, 122, 103517.
Salehi, H., & Burgueño, R. (2018). Emerging artificial intelligence methods in structural engineering. Engineering Structures, 171, 170–189.
Sun, H., Burton, H. V., & Huang, H. (2021). Machine learning applications for building structural design and performance assessment: State-of-the-art review. Journal of Building Engineering, 33, 101816.
Tamke, M., Nicholas, P., & Zwierzycki, M. (2018). Machine learning for architectural design: Practices and infrastructure. International Journal of Architectural Computing, 16(2), 123–143.
Tang, P., Huber, D., Akinci, B., Lipman, R., & Lytle, A. (2010). Automatic reconstruction of as-built building information models from laser-scanned point clouds: A review of related techniques. Automation in Construction, 19(7), 829–843.
Tian, J., Gao, M., & Zhou, S. (2009). The Research of Building Logistics Cost Forecast Based on Regression Support Vector Machine. 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, 1, 648–652.
Tooke, T. R., Coops, N. C., & Webster, J. (2014). Predicting building ages from LiDAR data with random forests for building energy modeling. Energy and Buildings, 68, 603–610.
Wang, Z., & Srinivasan, R. S. (2017). A review of artificial intelligence based building energy use prediction: Contrasting the capabilities of single and ensemble prediction models. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 75, 796–808.
Wu, S., & Sun, J. Q. (2011). A top-down strategy with temporal and spatial partition for fault detection and diagnosis of building HVAC systems. Energy and Buildings, 43(9), 2134–2139.
Zhang, C., Chang, C.-C., & Jamshidi, M. (2020). Concrete bridge surface damage detection using a single‐stage detector. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 35(4), 389–409.
Zhang, Y., Burton, H. V., Sun, H., & Shokrabadi, M. (2018). A machine learning framework for assessing post-earthquake structural safety. Structural Safety, 72, 1–16.
Zhao, H.-X., & Magoulès, F. (2012). A review on the prediction of building energy consumption. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(6), 3586–3592.
Zhao, Y., Li, T., Zhang, X., & Zhang, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence-based fault detection and diagnosis methods for building energy systems: Advantages, challenges and the future. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 109, 85–101.
Zhong, B., Pan, X., Love, P. E. D., Sun, J., & Tao, C. (2020). Hazard analysis: A deep learning and text mining framework for accident prevention. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 46, 101152.
Zhou, S., & Liu, D. (n.d.). Prediction of daylighting and energy performance using artificial neural network and support vector machine. In American Journal of Civil. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajcea-3-3A-1
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
