
ROS入門 (12) - ROS1のサービスによる通信
ROS1のサービスによる通信をまとめました。
・Melodic
前回
1. サービスによる通信
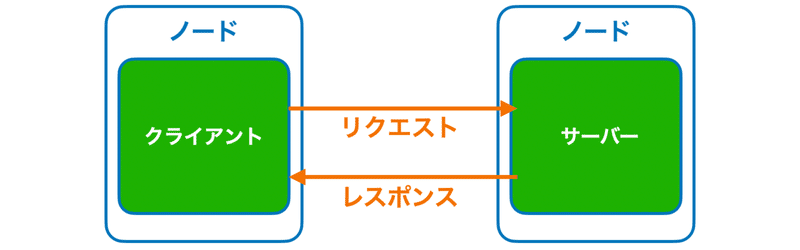
「サービス」は、「サーバー-クライアント」関係の通信を行います。クライアントがサーバーにリクエストすると、サーバーがレスポンスを返します。
2. ワークスペースのセットアップ
「ROS入門 (8) - ROS1のパッケージの作成」と同様です。
3. パッケージの作成
(1) 「~/catkin_ws/src」に移動し、「hello」という名前のパッケージを作成。
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src
$ catkin_create_pkg hello rospy std_msgs message_generation message_runtime・rospy : Pytonの利用
・std_msg : 標準メッセージの定義
・message_generation : メッセージのビルドに必要
・message_runtime : メッセージの実行に必要
(2) 「CMAkeLists.txt」を以下のように編集。
・50行目あたり
利用するサービスファイル名を指定します。
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder
add_service_files(
FILES
AddTwoInts.srv
)・70行目あたり
サービスの生成を指定します。
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here
generate_messages(
DEPENDENCIES
std_msgs
)4. サービスファイルの作成
「サービスファイル」は、サービスのデータ型を記述するテキストファイルです。拡張子は「.srv」です。パッケージのsrvフォルダで保持します。
(1) 「~/catkin_ws/src/hello/srv/AddTwoInts.srv」を作成し、以下のように編集。
・AddTwoInts.srv
int64 a
int64 b
---
int64 sum1行毎にデータ型と変数名を記述します。「---」より上はリクエスト、下はレスポンスの情報になります。
指定可能なデータ型は、次のとおりです。
・int8、int16、int32、int64 (plus uint*)
・float32、float64
・string
・time、duration
・他のmsgファイル
・可変長のarray[]、固定長のarray[C]
5. ソースコードの作成
(1) 「~/catkin_ws/src/hello/src/client.py」を作成し、以下のように編集。
・client.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: UTF-8
import rospy
from hello.srv import *
# リクエストの送信
def add_two_ints_client(x, y):
rospy.wait_for_service('add_two_ints')
try:
add_two_ints = rospy.ServiceProxy('add_two_ints', AddTwoInts)
resp1 = add_two_ints(x, y)
return resp1.sum
except rospy.ServiceException as e:
print "Service call failed: %s"%e
# メイン
def main():
x = 1
y = 2
print "%s + %s = %s"%(x, y, add_two_ints_client(x, y))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()(2) 「~/catkin_ws/src/hello/src/server.py」を作成し、以下のように編集。
・server.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: UTF-8
import rospy
from hello.srv import *
# リクエストの受信に呼ばれる
def handle_add_two_ints(req):
return AddTwoIntsResponse(req.a + req.b)
# メイン
def main():
# ノードの初期化
rospy.init_node('add_two_ints_server')
# サーバーの開始
s = rospy.Service('add_two_ints', AddTwoInts, handle_add_two_ints)
# ノード終了まで待機
rospy.spin()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()(3) 「client.py」「server.py」が実行できるようにモード指定。
$ chmod u+x client.py
$ chmod u+x server.py(3) ワークスペースのビルド。
$ cd ~/catkin_ws
$ catkin build(4) ワークスペースのセットアップ。
ワークスペースのセットアップはビルド毎にも必要になります。
$ source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash6. 実行
(1) ターミナルを開き、「roscore」を実行。
$ roscore(2) もう1つのターミナルを開き、「server」を実行。
クライアントからリクエストを受け取る準備ができました。
$ rosrun hello server.py(3) もう1つのターミナルを開き、「client」を実行。
2つの値がサーバーに渡され、計算結果が返されます。
$ rosrun hello client.py
1 + 2 = 37. 参考
次回
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
