
[FAR] Lease Accounting について ④
さて、今回は Lessor 側 から見た種類別の Account 方法についてと、Guaranteed、Unguaranteed について解説していけたらなと思います。
何を言っているか意味が分からないかもしれませんが、とりあえずお付き合いください。
ではよろしくお願いします。
大まかな種類分け

Lessor(貸し手)は以下の3つの内どれかに当てはめて Journal Entry をしていきます。今回は特にこと中野 Direct Lease について見ていきましょう。
(Operating Lease と Sales-type Lease 関しては前回の記事を参照してください)
Direct Financing Lease について
そもそも Direct Financing Leaseって他の2つと何が違うんだろうということなんですが、Direct Financing Lease は主に、interest (利息)から利益を生み出すという方法です。よって、大抵の場合この Direct financing lease は 金融機関によって行われます。
では今日も例題を使って見ていきましょう。
以下の会社は金融系の貸し出し会社とします。
Your company leases a machine for 3 years to ABC company. Your company will make a lease payment of $20,000 at the beginning of each year. The machine is expected to have a useful economic life of 10 years, and your company uses a straight-line method for depreciation.
The cost basis for the machine is $50,000 (Inventory).
The expected salvage value of the machine is zero.
The lessor's implicit interest rate is 6%.
PV of residual Value = $12,594
PV of lease payment = $56,668
Fair Value of Machine = $69,262

この場合、Journal Entry はこのような形になります

私たちは Lessor 側なので当然 Inventory は Cr 側にして、在庫を減らします。Deferred growth profit は plug ナンバーだと思ってください。数合わせのためにあると考えてもらって構いません。
Guaranteed Residual Value とは?
次は Lesseeの視点から Guaranteed Residual Value について見ていきたいと思います。
まずこれはどういったものかというと、
あなたが Lessee (借り手)だとし、machine を借りたときに、返す最後の日におけるこのmachine の residual value が最低でも $10,000 くらいになると考えたとします。さてその時、lease liabilityにどう影響があるのかを感がて行きましょう、というものです。
つまり、Residual Value がわかるとき、それは Guaranteed Residual Value と見なし、Lease liability に含める必要があるのです。
では、どのように Guaranteed であり、いつ含めるのかを見ていきましょう。
Unguaranteed residual value → do not include in the lease liability
Expected RV > Guaranteed RV → do not include in the lease liability
e.g. ERV =$20,000 の場合、 Guaranteed RV は $10,000 であった場合は、liabilityとして認識しなくていいんです。
Expected RV < Guaranteed RV → include lease liability
e.g. ERV = $5000 の場合、10,000 - 5,000 = 5000 の PV を計算し、その額を Liability として計上します。
例題を使って…
Your firm is a lessee on a finance lease.
You do the lease for 3 years, and the lessor's incremental borrowing rate is 6%. Guaranteed Residual value is $15,000. Your company will make a lease payment of $20,000 at the beginning of each year. PV of residual Value is $12,594,
The lease payment's PV is $56,668, and the asset being leased's fair value is $69,262. Expected Residual Value is $10,000.
The difference between GRV and ERV is $5,000, and the present value of the probable residual payment is $4,198.
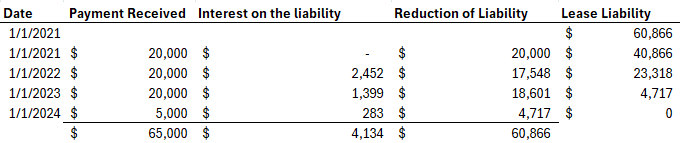
5000 は最後 Lessor に返すためのものです。GRV - ERV
今回は、ERV < GRV であるため、 Lease liability を含める必要があります。
Journal Entry は以下のようになります。
2年目、3年目は1年目と同じ繰り返しになるので省略しました。

以上が Guaranteed の場合でした。
Unguaranteed の計上方法とは? Lessor 側の視点で解説
ここでいう Unguaranteed とは上でも書きましたが、 Unguaranteed residual value のことです。
今回の場合、自分は貸し手で、例えば Machine の残存額が $20,000 になるだろうと考えました。しかし借り手側から何の guarantee がなければ当然これは Unguaranteed になるわけです。
例を使って見ていきましょう
Your firm is a lessor on a 3 years of sales-type lease.
The lessor's incremental borrowing rate is 6%.
Unguaranteed Residual value is $15,000. Your company will receive a lease payment of $20,000 at the beginning of each year. PV of unguaranteeed residual Value is $12,594,
The lease payment's PV is $56,668, and the asset being leased's fair value is $69,262.
The cost basis is $50,000.
僕らは Lessor 側として $15,000 Residual value として Machine が残るだろうと考えました。しかし Lessee 側はそれを Guarantee してくれていません。
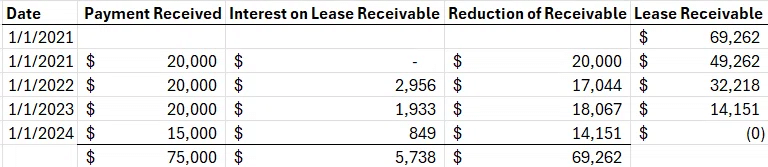
図1をもとに Journal Entryを作成すると

ここで注目すべきは Lease Rec / Sales Rev の数値が違うことです。
Sales Rev に何が起きているかというと、Fair Value of Asset から Unguaranteed 分の 12,594 が差し引かれているのです。Guarantee されているかわからないので、とりあえず含めないことにするのです。
当然 Inventory は Cost basis を反映しているので 50,000 であり、COGS も 50,000 であるはずなのですが、 Unguaranteed 分の 12,954を含めないので、
50,000 - 12,954 = 37,406 になっています。
さて、ここで Unguaranteed Residual Value is $15,000 but assume the asset is only worht $7,000 になったとしましょう。
つまり、 Lessee側がなんの Guarantee もしてくれなかったので、ふたを開けてみたら Machine の価値が $7,000 だけになっていました。
この場合、当然 15,000 と予測していた点から 実際は $7,000 になっていたので loss が発生します。よって…
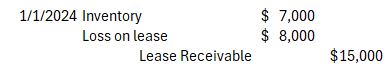
比較の Journal Entry
左が普通の Sales type, 右が Unguaranteed のJRです

Bargain Purchase Option があることだけでも覚えて帰って!!
長い旅お疲れさまでした。
これが最後の lease についての話になります。
Bargain Purchase Option というものを Lessee の視点から解説していきたいと思います。
Bargain Purchase Optionとは何でしょうか?
これは、借り手 (lessee) がリース期間終了時にリース資産をその Fair Market Value (公正市場価格) を大幅に下回る価格で購入することを認める方法です。
ここでもう一つ気を付けないといけないのが、 lessee は Asset を Lease term ではなく Economic lifeで Amortizes しなくてはいけません。これは、Lease termが終わってから Lesseeは 安い価格で Lease したものを購入するためです。つまり Ownershipが移行するからです。
例題
Your firm is a lessee on a finance lease and lease term is 3 years.
The lessor's incremental borrowing rate is 6%.
Unguaranteed Residual value is $15,000.
Your company will make a lease payment of $20,000 at the beginning of each year. PV of unguaranteeed residual Value is $12,594,
The lease payment's PV is $56,668, and the asset being leased's fair value is $69,262.
The bargain purhcase option is $5,000.
PV of bargain purchase option is $4,198
Economic life time is 4 years.
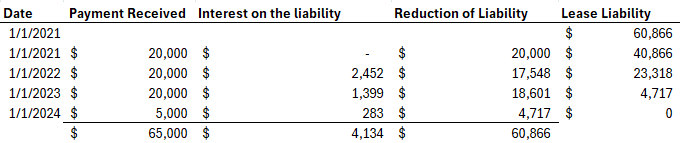
PVの Bargain Option と lease payment として支払う 56,668を足し合わせています。
すると、Journal Entry は以下のようになります。 Amortization Expは4年で割られていることに注意してください。

最後は、Ownershipがこちら側に移ったので、当然普通に Depreciation としてカウントしないといけません。よって12/31/2024 にも計上されています。
以上でリースの話はおしまいです。
お疲れさまでした!
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
