
パーマン1号・声優・三輪勝恵さん、急性肺塞栓のため死去 80歳
声優でナレーターの三輪勝恵さんが、急性肺塞栓のため6月19日に死去した。80歳。1日に所属する「青二プロダクション」が報告した。
サイトでは「弊社所属 三輪勝恵 儀 (80歳)去る令和6年6月19日に急性肺塞栓のため永眠いたしました」と伝え「ここに生前賜りましたご厚誼を深謝し謹んでご通知申し上げます」と記した。
一言で言えば、肺の血管に血管が詰まって呼吸不全を引き起こす病気です。病名そのままですね。
90%は、下肢の血管でできた血栓が流れてきて詰まったものです。
Acute Pulmonary Embolism Following Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination - A Case Report and Literature Review
Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2ワクチン接種後の急性肺塞栓症 - 症例報告と文献レビュー
https://www.tsoc.org.tw/upload/journal/1/20220731/acs-38-539.pdf
INTRODUCTION
In the era of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic, vaccination has become an important and urgent need worldwide. Despite the development of vaccines, their safety is still a common concern among the public. Thromboembolism is a safety concern with these vaccines, especially adenovirus (AstraZeneca) vaccines. However, although not rarely reported, mRNA vaccines have also been associated with the risk of thromboembolism, especially in East Asian populations. Herein, we describe a previously asymptomatic patient who presented with acute pulmonary embolism shortly after receiving the Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
はじめに
新型コロナウイルス(SARS-CoV-2)パンデミックの時代において、ワクチン接種は世界中で重要かつ緊急のニーズとなっています。ワクチンの開発にもかかわらず、その安全性は依然として一般の人々の間で共通の懸念事項となっています。血栓塞栓症は、これらのワクチン、特にアデノウイルス(アストラゼネカ)ワクチンの安全性に関する懸念事項です。しかし、mRNAワクチンも、特に東アジアの集団において血栓塞栓症のリスクと関連付けられています。ここでは、モデルナmRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2ワクチン接種後まもなく急性肺塞栓症を呈した、以前は無症状であった患者について説明します。
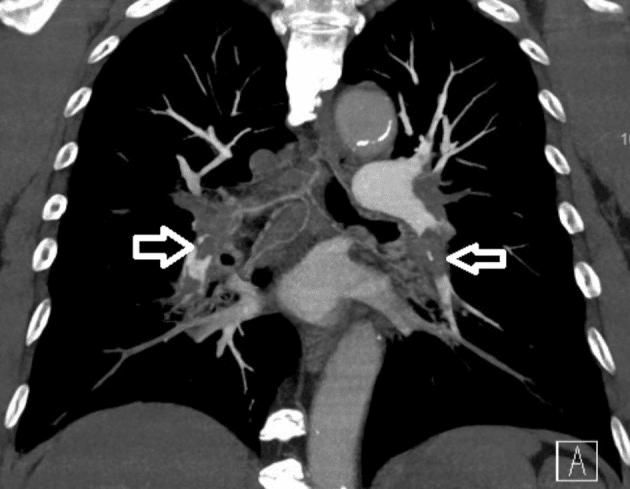
コンピュータ断層撮影血管造影検査で両側肺塞栓症が確認されました(白い矢印)。
CASE
This case was a 70-year-old East Asian male, a current smoker, with a past medical history of hypertension and an old cerebrovascular accident, with independent activities of daily living. He received the first dose of the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine 5 weeks prior to this episode. He presented to our emergency department with progressive shortness of breath for 5 days. A physical examination revealed blood pressure of 120/70 mmHg, heartbeat of 102 beats per min, and SpO2 around 90%. Resting 12-lead electrocardiography revealed sinus tachycardia and a typical S1Q3T3 pattern. Laboratory data showed normal platelet count, hemoglobin and fibrinogen levels. A SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction was negative. The D-dimer level was 4895 ng/mL, and chest computed tomography angiography showed bilateral saddle pulmonary embolism (Figure 1).
症例
この症例は、70歳の東アジア系男性で、現在喫煙者であり、高血圧および脳血管障害の既往歴はありますが、自立した日常生活を送っていました。この症例の5週間前に、モデルナmRNA-1273ワクチンの初回接種を受けた。5日間にわたる進行性の息切れを主訴として、当院救急外来を受診した。身体検査の結果、血圧120/70mmHg、心拍数102回/分、SpO2約90%であった。安静時12誘導心電図では、洞性頻脈および典型的なS1Q3T3パターンが認められた。臨床検査データでは、血小板数、ヘモグロビン、フィブリノーゲン値は正常であった。SARS-CoV-2ポリメラーゼ連鎖反応は陰性であった。Dダイマー値は4895ng/mLであり、胸部CT血管造影では両側の鞍型肺塞栓症が認められた(図1)。
To further survey the pulmonary embolism, we conducted examinations in order to verify the possible etiology, including autoimmune disease markers (including antinuclear antibody, C3, C4, lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin immunoglobulin), tumor markers (including CEA, alpha-fetal protein, CA199, and PSA), coagulant function tests (including protein C function, antithrombin III, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time), all of which were within normal limits. Protein S function was 25.4% (normal value 62.6-150.4%) and the anti-platelet factor 4 (PF4) antibody titer was 50.01 ng/ml (cutoff value of 50 ng/ml) with an optical density of 0.424 units (weakly positive, cutoff value of 0.4 units). Left popliteal vein thrombosis was found by peripheral Doppler sonography (Figure 2).
肺塞栓症のさらなる調査のため、考えられる病因を確認するための検査を実施し、自己免疫疾患マーカー(抗核抗体、C3、C4、ループス抗凝固因子、抗カルジオリピン免疫グロブリンなど)、腫瘍マーカー(CEA、α胎児性タンパク質、CA199、PSAなど)、凝固機能検査(プロテインC機能、アンチトロンビンIII、プロトロンビン時間、部分トロンボプラスチン時間など)はすべて正常範囲内でした。プロテインS機能は25.4%(正常値62.6~150.4%)、抗血小板因子4(PF4)抗体価は50.01 ng/ml(カットオフ値50 ng/ml)、光学密度は0.424単位(弱陽性、カットオフ値0.4単位)でした。末梢ドップラー超音波検査により左膝窩静脈血栓症が発見されました(図2)。

末梢ドップラー検査では、右膝窩静脈に部分的な閉塞を伴う血栓の可能性が明らかになりました (白い開いた矢印)。
He was initially treated with low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin sodium) for the first 3 days, and direct oral anticoagulants (dabigatran 110 mg twice daily) was added thereafter because vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) was highly suspected. The symptoms gradually improved, and he was discharged 7 days later uneventfully. He is still asymptomatic 3 months after the episode with regular follow-up at the outpatient department and direct oral anticoagulant treatment.
最初の3日間は低分子量ヘパリン(エノキサパリンナトリウム)で治療し、その後はワクチン誘発性免疫血栓性血小板減少症(VITT)が強く疑われたため、直接経口抗凝固薬(ダビガトラン110mgを1日2回)を追加しました。症状は徐々に改善し、7日後に何事もなく退院しました。エピソードから3か月経った現在も無症状で、外来で定期的に経過観察と直接経口抗凝固薬による治療を受けています。
DISCUSSION
In this report, a previously healthy East Asian patient without known risk factors for thromboembolic disorder presented with acute pulmonary embolism 5 weeks after receiving the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine. After a series of studies, we found that the possible etiology for left popliteal deep vein thrombosis and bilateral pulmonary embolism was VITT, which was confirmed by weakly positive anti-PF4 antibodies and protein S deficiency.
In previous reports of thromboembolic events after mRNA vaccines, a large self-controlled case series study in England reported increased risks of both hematological and thromboembolic events within 2 to 3 weeks after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 mRNA vaccines.1 Venous thromboembolism has seldom been reported with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Moreover, these risks are much lower compared to those with SARS-CoV-2 infection based on a recent meta-analysis.2 However, in our case, acute pulmonary embolism developed more than 5 weeks after vaccination. A possible explanation is the thromboembolism originated from left popliteal vein thrombosis initially after vaccination, and then the thrombus gradually migrated into bilateral pulmonary trunk 2 to 3 weeks later.
考察
本報告では、血栓塞栓症の既知のリスク因子のない、以前は健康であった東アジアの患者が、Moderna mRNA-1273ワクチン接種後5週間で急性肺塞栓症を発症した。一連の研究の後、左膝窩深部静脈血栓症および両側肺塞栓症の考えられる病因はVITTであることが判明し、これは抗PF4抗体の弱陽性およびプロテインS欠乏によって確認された。
mRNAワクチン接種後の血栓塞栓症に関するこれまでの報告では、イギリスで行われた大規模な自己対照症例シリーズ研究で、ChAdOx1 nCoV-19およびBNT162b2 mRNAワクチン接種後2~3週間以内に血液学的および血栓塞栓症の両方のリスクが上昇することが報告されている。1 BNT162b2 mRNAワクチンでは静脈血栓塞栓症が報告されることはほとんどない。さらに、最近のメタアナリシスによると、これらのリスクはSARS-CoV-2感染者に比べてはるかに低いとのことです。2 しかし、今回の症例では、ワクチン接種後5週間以上経ってから急性肺塞栓症を発症しました。考えられる説明としては、ワクチン接種後、最初は左膝窩静脈血栓症から血栓塞栓症が発生し、その後2~3週間後に血栓が徐々に両側の肺幹に移動したと考えられます。
The most common mechanism of VITT is a heparin-induced thrombocytopenia-like pathway related to anti-PF4 antibodies. This mechanism has also been reported in adenovirus vector and RNA vaccines,3,4 however it has also been reported in mRNA vaccines.5 The mechanism by which the immune response after vaccination leads to the formation of anti-PF4 antibodies is poorly understood. A recently published case series showed no strong correlations between the levels of PF4-heparin antibodies and anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. In addition, no significant difference in the level of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies has been found between patients with and without thrombus formation.6
It is currently unclear how long pathogenic anti-PF4 antibodies persist. In a study involving 35 patients with serologically confirmed VITT, levels of anti-PF4 antibodies were found to gradually decline but could exist for more than 12 weeks in some cases.7 In our case, the level of anti-PF4 antibodies was only weakly elevated at the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, which may be related to a decline in anti-PF4 antibodies due to the time interval from vaccination (5 weeks).
Interestingly, one case report reported a relationship between vaccination and autoimmune disorders, in which positive antiphospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulants were demonstrated.8 A similar phenomenon has been observed in patients with COVID-19 infection.9 Nevertheless, in our patient, protein S deficiency was observed with normal antiphospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulants. This has never been reported in other studies, and the relationship between protein S and COVID-19 vaccine is unknown. We hypothesize that a COVID-19 vaccine may be the trigger for thrombosis in a patient with protein S deficiency.
For patients with vaccine-induced thrombosis, the use of direct oral anticoagulants has been recommended in order to avoid initial heparin therapy which may aggravate VITT. The administration of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin or dexamethasone may also be helpful.10 We immediately switched enoxaparin sodium to dabigatran in our case after excluding other etiologies. However, the duration of anticoagulant therapy is not well understood. Whether it should be treated as unprovoked pulmonary embolism is still under debate, and further studies are needed to guide treatment.
VITT の最も一般的なメカニズムは、抗 PF4 抗体に関連するヘパリン誘発性血小板減少症のような経路です。このメカニズムは、アデノウイルスベクターワクチンおよび RNA ワクチンでも報告されていますが、3,4 mRNA ワクチンでも報告されています。5 ワクチン接種後の免疫反応が抗 PF4 抗体の形成につながるメカニズムは十分に理解されていません。最近発表された症例シリーズでは、PF4 ヘパリン抗体と抗 SARS-CoV-2 IgG 抗体のレベルに強い相関関係は見られませんでした。さらに、血栓形成のある患者とない患者の間で抗 SARS-CoV-2 IgG 抗体のレベルに有意な差は見られませんでした。6
病原性の抗 PF4 抗体がどのくらいの期間持続するかは、現在のところ不明です。血清学的にVITTが確認された35人の患者を対象とした研究では、抗PF4抗体のレベルは徐々に低下しているが、場合によっては12週間以上存在する可能性があることが判明しました。7私たちのケースでは、肺塞栓症の診断時に抗PF4抗体のレベルはわずかに上昇しただけで、これはワクチン接種からの期間(5週間)による抗PF4抗体の低下に関連している可能性があります。
興味深いことに、ある症例報告では、ワクチン接種と自己免疫疾患の関係が報告されており、抗リン脂質抗体とループス抗凝固因子が陽性であることが示されました。8同様の現象がCOVID-19感染患者でも観察されています。9しかし、私たちの患者では、抗リン脂質抗体とループス抗凝固因子は正常で、プロテインS欠乏症が観察されました。これは他の研究では報告されておらず、プロテインSとCOVID-19ワクチンの関係は不明です。 COVID-19ワクチンがプロテインS欠乏症患者の血栓症の引き金になる可能性があると我々は仮説を立てている。
ワクチン誘発性血栓症の患者には、VITTを悪化させる可能性のある初期のヘパリン療法を避けるために、直接経口抗凝固薬の使用が推奨されている。高用量の静脈内免疫グロブリンまたはデキサメタゾンの投与も役立つ可能性がある。10 我々の症例では、他の病因を除外した後、すぐにエノキサパリンナトリウムからダビガトランに切り替えた。しかし、抗凝固療法の期間はよくわかっていない。これを誘発性のない肺塞栓症として治療すべきかどうかはまだ議論の余地があり、治療の指針となるさらなる研究が必要である。
コロナワクチンと急性肺塞栓症: J Clin Medに掲載された論文から
荒川央 (あらかわ ひろし)
2022年7月5日 03:05
荒川央先生いわく
コロナワクチンに使われるスパイクタンパクは血管毒性を持ち、血栓の原因となります。スパイクタンパクによる血栓が肺に達したものが肺塞栓症と考えられます。こうした作用機序からコロナワクチンは、肺塞栓症の潜在的な危険因子となります。
血栓症の発症とワクチン接種のタイミングは非特異的です。血栓症の多くは7〜10日目に発症する事が報告されていますが、本例は初回接種から4週間後、2回目の接種から8日以内に発症しました。このように、血栓ができるタイミングはワクチン接種すぐとは限らず、遅れて発症する事もあります。
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
