ヒスタミンH1、H2受容体のinverse agonist効果を通したcrossregulation
某抗ヒスタミン薬剤の宣伝でinverse agonist作用があった
ちょっと解説が違うのではないかと思い、ちょっと調べてみた
H3、H4がらみが主体のようだ
他、ヒスタミンH1、H2受容体のinverse agonist効果を通したcrossregulationが記載されていた
what is inverse agonists?
PERPLEXITY
An inverse agonist is a ligand that binds to the same receptor-binding site as an agonist and produces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist[1][2]. Inverse agonists bind with constitutively active receptors, stabilize them, and reduce their activity[3][4]. They are distinct from antagonists in that they produce an effect rather than simply blocking the action of an agonist[5].;アゴニストと同じ受容体結合部位に結合し、アゴニストとは逆の薬理学的反応を引き起こすリガンド。
逆作動薬が作用する前提として、標的受容体はリガンドが結合していない状態でも常時活性(内活性(英語版)または基礎活性として知られる)を有している必要がある。作動薬は受容体の基礎活性を増加させ、逆作動薬は基礎活性を低下させる。
完全作動薬の活性(英語版)が100%、(純粋な)遮断薬の活性が0%であるとすると、逆作動薬の活性は0%未満(マイナス)である。
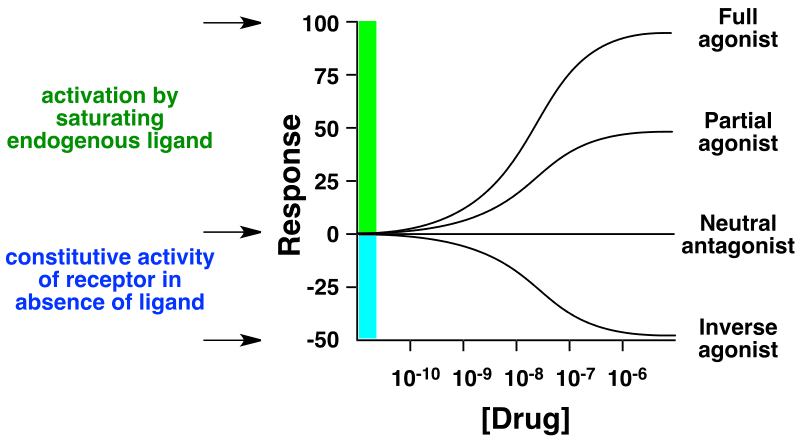
”H1抗ヒスタミン薬”全般が"inverse antagonist"のようで、なんか騙されたような気がするなあ
Tiligada E, Ennis M. Histamine pharmacology: from Sir Henry Dale to the 21st century. Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;177(3):469–89. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7012941/
Moreover, the advances in molecular biology in the 1990s led to the concept of constitutive receptor activity that directed the reclassification of GPCR antagonists as inverse agonists that can reduce constitutive activity, or neutral antagonists, which do not affect the basal receptor activity but interfere with agonist binding (Leurs et al., 2002). Since H1 antihistamines may be inverse agonists or neutral antagonists, this therapeutic drug class is commonly referred to by the suggested term ‘H1 antihistamines’ rather than ‘H1 antagonists’ (Leurs et al., 2002; Church and Church, 2013).;さらに、1990年代の分子生物学の進歩により、受容体活性が構成的であるという概念が生まれ、GPCRアンタゴニストは、構成的な活性を減少させることができるインバースアゴニスト、または基底の受容体活性に影響を与えないがアゴニスト結合に干渉するニュートラルアンタゴニストに分類し直した(Leursら、2002年)。H1抗ヒスタミンは、逆作用薬または中性拮抗薬である可能性があるので、この治療薬クラスは、一般に、「H1拮抗薬」ではなく「H1抗ヒスタミン」という提案用語で呼ばれる(Leursら、2002;ChurchおよびChurch、2013)。
ヒスタミンH1、H2受容体のinverse agonist効果を通したcrossregulationに注目した研究で、ヒスタミンH1とH2受容体のメカニズムについて新しい知見が判明し、inverse agonists治療への新しい応用法に役立つのかもしれない

Histamine [2-(4-Imidazolyl)-ethylamine] はヒスタミンH1やH2受容体を通して、異なる生物学的プロセスを調整し、それぞれの遮断薬が広くアレルギーや胃酸関連疾患へ用いられている。 ヒスタミンH1とH2受容体のcrossdesensitization や cointernalizationは以前から記載されてきた。desensitization assayにより、ヒスタミンH1およびH2受容体インバースアゴニストが両受容体間のcrossregulationを誘導することを証明した。この意味で、ヒスタミンH1受容体inverse agonistは、ヒスタミンH2受容体 agonistであるamthamineのcAMP応答を脱感作するのである。その結果、ヒスタミンH2受容体 inverse agonistは、ヒスタミンH1受容体のシグナル伝達を阻害することがわかった。また、ヒスタミンH1またはH2受容体agonistによって誘導される交差増感作用がヒスタミン inverse agonist受容体の応答を変化させることを決定した。ヒスタミンH1受容体の活性化はヒスタミンH2受容体逆アゴニストによって誘導されるcAMP応答に対して影響を与え、一方ヒスタミンH2受容体アゴニストはヒスタミンH1受容体 inverse agonistの抗炎症応答に対して負の調節作用を誘発する。binding studyによりヒスタミンH1とH2受容体がヒスタミン受容体inverse agonist刺激後cointernalizeすることが明らかになった。また、 internalization process の阻害により、受容体のreceptor crossregulationが抑制されることがわかった。本研究は、ヒスタミンH1およびH2受容体 inverse agonistの効果を説明するヒスタミンH1およびH2受容体の作用機序に新しい洞察を与え、新規治療法への応用の場を開くものである。
Translated with DeepL
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
