EBBXライブラリを使った機能強化版インジケータ(202408版)
はじめに
先日リンク先で紹介したsample_ebbxは、TradingViewでEBBXをとりあえず動かす方法を説明するための単純なものでした。今回は機能の強化をして実用的にしていきます。出来上がった300行を超えるソースを末尾につけておきます。
変化がほぼなければ判定が変わらないようにする
前回のsample_ebbxでは、e1pが直前より上かどうかで強気かどうか判定しているため、値の変化がほぼなくても判定が変わることがあります。そこで今回は、上昇し続けたe1pが下がり始めても、e1pのピークからある程度下がるまで弱気に切り替わらないという仕様にしました。(わざわざ触れないことが多いですが、底からある程度上がらないと、という上下逆の話も同様です。)
marginの計算
指数重み標準偏差であるe0dを価格変動幅の基準として使い、e0dのx%だけ下がったら弱気になることにします。このx%をmarginと呼びます。gが大きいほど価格変動のノイズが相殺され、このmarginは小さくできるはずです。大雑把な実験の結果、g=1mでmarginは10%、gが256倍になったらmarginは半分としました。次のget_margin()でそのmarginを計算しています。pow()とかlog()のところはプログラムでは複雑そうですが、中心部分ではこの値を計算しています。$${ 0.5^\frac{\log \mathrm{g\_in\_minutes}}{\log 256} = 0.5^{log_{256} \mathrm{g\_in\_minutes}} }$$
// @function e1pの方向の計算で使うmarginを計算する
// @param g_in_minutes 分単位で表したg
// @returns e0dに対する割合を表すmargin
export get_margin(float g_in_minutes) =>
// g_in_minutes=1のとき0.1(つまり10%)を返す
// g_in_minutes=256のとき0.05、256^2のとき0.025と、256倍になるたび0.5倍になる
0.1 * math.pow(0.5, math.log(g_in_minutes)/math.log(256))主なgでのmarginは次の通りです。
$$
\begin{array}{|r r|} \hline
\mathrm{g} & \mathrm{margin} \\ \hline
\mathrm{1m} & 10.0% \\
\mathrm{1h} & 6.0% \\
\mathrm{1D} & 4.0% \\
\mathrm{1W} & 3.3% \\
\mathrm{1M} & 2.7% \\
\mathrm{1Y} & 2.0% \\ \hline
\end{array}
$$
ポジションposの計算
e1pがピークからe0d*marginだけ下がったら、という処理を行っているのは次の部分です。
// @function e1pの向きとe1pとe0pの上下関係でポジションを計算する
// @param e1p ebbxのe1p
// @param e0p ebbxのe0p
// @param e0d ebbxのe0d
// @param margin e1pの方向判定で、逆行を e0d*margin まで許す
// @returns ポジション(+2, +1, -1, -2)
export get_ebbx_pos(float e1p, float e0p, float e0d, float margin) =>
var dir = +1 // e1pの向き(+1 上向き、-1 下向き)
var h = e1p // e1pの直近高値
var l = e1p // e1pの直近安値
dir :=
less_than(e1p, h-e0d*margin) ? -1 : // 直近高値-e0d*marginをe1pが下回れば下向き
more_than(e1p, l+e0d*margin) ? +1 : // 直近安値+e0d*marginをe1pが上回れば上向き
dir
h := dir > 0 ? math.max(h, e1p) : e1p // 上向きのとき直近高値をmath.max(h, e1p)で更新
l := dir < 0 ? math.min(l, e1p) : e1p // 下向きのとき直近安値をmath.min(l, e1p)で更新
pos = dir > 0 ? // dirが正なら強気
more_than(e1p, e0p) ? +2 : +1 : // e1p > e0pだとより強気
less_than(e1p, e0p) ? -2 : -1 // e1p < e0pだとより弱気e1pの方向のdir、直近高値(ピーク)のh、直近安値のlを保持しています。
dirが上向きの場合、e0p*marginでハンデをつけた直近高値よりe1pが小さい
とdirを切り替えています。
出力する値posは+2、+1、-1、-2をとり、大きいほど強気です。
dirが上向きのとき、e1p>e0pなら+2、e1p≦e0pなら+1で、
dirが下向きのとき、e1p<e0pなら-2、e1p≧e0pなら-1です。
参考までに、前回のsimple_ebbxと同じ動作をするget_ebbx_pos_simple()も作っておきました。
色の塗り分け
posから塗る色への変換は次のコードで行っています。
関数本体では色指定が省略された場合の処理の後、posによって色が選択されています。
インジケータの計算開始からの期間が十分ない段階ではEBBXの各値の精度が低いです。not_enough=trueにしておけば色をつけないようにしてあります。
// @function ポジションで4色に塗り分ける
// @param pos ポジション
// @param not_enough 経過時間が短いので色分けしない
// @param color_bull0 弱買の色
// @param color_bull1 買の色
// @param color_bear0 弱売の色
// @param color_bear1 売の色
// @returns 選択された色
export pos2col4(int pos, bool not_enough=false, color color_bull0=na, color color_bull1=na, color color_bear0=na, color color_bear1=na) =>
var col_bull0 = nz(color_bull0, red(tune_s=-80, tune_v=+100)) // 弱買
var col_bull1 = nz(color_bull1, red(tune_s=-50, tune_v=+70)) // 買
var col_bear0 = nz(color_bear0, blue(tune_s=-80, tune_v=+100)) // 弱売
var col_bear1 = nz(color_bear1, blue(tune_s=-50, tune_v=+70)) // 売
not_enough ? na :
pos > 0 ? pos > 1 ? col_bull1 : col_bull0 :
pos < 0 ? pos < -1 ? col_bear1 : col_bear0 :
na // pos == 0 のとき3色に塗り分けるpos2col3()もあります。どちらも引数で好みの色に変えることもできます。
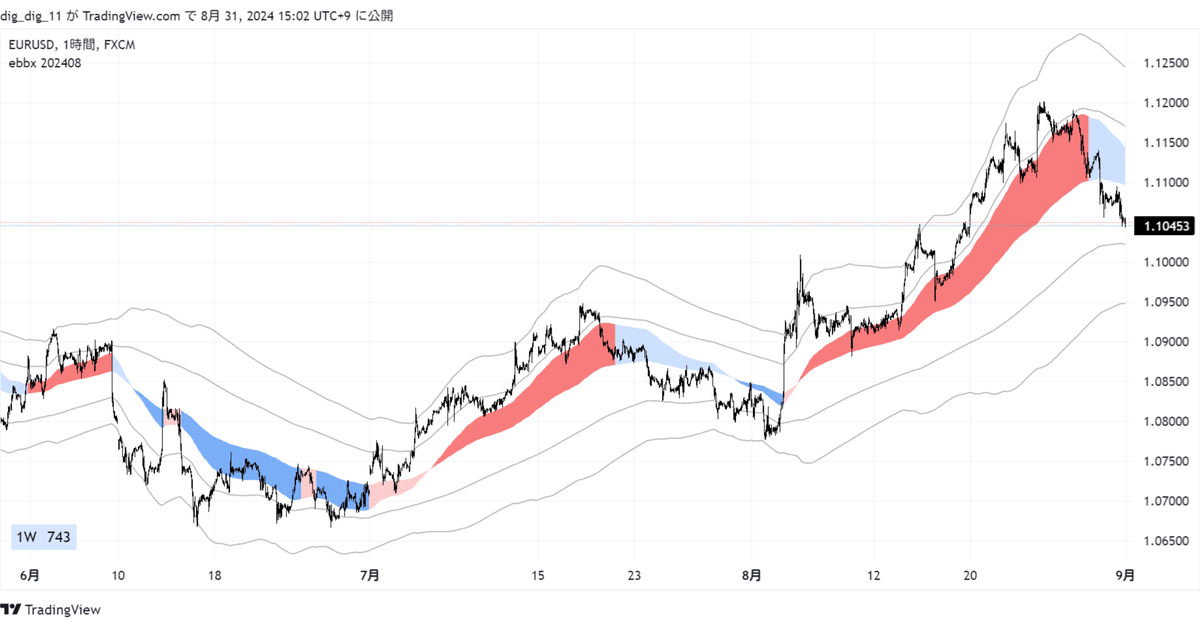
前回と今回のチャートは次のようになります。


e1pの傾きが0を前後するときに前回のsimple ebbxでは何度も色が変わっていましたが、今回のebbx 202408では期待通り同じ色が続いています。
情報テーブルの追加
情報テーブルの追加もしました。上のチャートで情報テーブルは左下にあり、1Wというのはgの値です。そこにカーソルを合わせるとg=120bars margin=3.3%という情報が出てきます。テーブルに表示するものをa_strに、ツールチップで表示するものをa_str_ttに入れて次の関数を呼ぶことで実現しています。引数を指定することで情報テーブルの位置、文字の大きさや色などが変えられます。
情報テーブルの2553というのは現在のe0dの値です。mintickで2553個分、約2.5円ということです。この値はインジケータのソースから、リアルタイム更新されています。
// @function 指定されたテーブルを作る
// @param a_str テーブルに表示する文字列の配列。横優先で入れる。データがなくても""などを入れる
// @param a_str_tt ツールチップで表示する文字列の配列。横優先で入れる
// @param columns テーブルの幅(extra_spaceは含まない)
// @param position テーブルの表示位置 position.top_left, position.top_center, position.top_right, position.middle_left, position.middle_center, position.middle_right, position.bottom_left, position.bottom_center, position.bottom_right
// @param bgcolor 背景色
// @param text_color 文字列の色
// @param text_size 文字列の大きさ size.auto, size.tiny, size.small, size.normal, size.large, size.huge
// @param text_halign 横方向の配置方法 text.align_left, text.align_center, text.align_right
// @param extra_space 左に場所を空けるかどうか
// @returns 生成されたテーブル
export get_table(array<string> a_str, array<string> a_str_tt=na, int columns=1,
string position=position.bottom_left,
color bgcolor=na,
color text_color=na,
string text_size=size.normal,
string text_halign=text.align_right,
bool extra_space=false) =>
var col = nz(text_color, black())
var col_bg = nz(bgcolor, gray(95))
var count = array.size(a_str)
var count_tt = na(a_str_tt) ? 0 : array.size(a_str_tt)
var rows = count / columns
var tbl = table.new(position, 1+columns, rows) // カラム0はextra_space用に追加
if extra_space
tbl.cell(0, 0, text=" ", text_size=size.small) // 場所を空けるため
for y = 0 to rows-1
for x = 0 to columns-1 // 横優先で入っているので、内側ループでは横を連続して処理
index = y*columns + x
if index < count
tbl.cell(1+x, y, text=array.get(a_str, index), text_size=text_size, text_halign=text_halign, text_color=col, bgcolor=col_bg)
if index < count_tt
tbl.cell_set_tooltip(1+x, y, array.get(a_str_tt, index))
tblgを指定するときの単位に、h、Wなどを追加
simple_ebbxでは、barの数でしかgを指定できませんでした。今回は、gの単位としてb(barの数)だけでなく、s(秒)、m(分)、h(時間)、D(日)、W(週)、M(月)、Y(年)も指定できるようにしました。

次の関数で実現しています。
// 週7日動いている市場などでは変えたほうがよい
get_hours_in_day() => 24
get_days_in_week() => 5
get_days_in_month() => 21
get_days_in_year() => 259
// @function 値と単位からbarの数に換算する
// @param f 値
// @param unit 単位
// @returns 換算されたbarの数
export readable2bars(float f, string unit) =>
var hid = get_hours_in_day()
var timeframe = timeframe.in_seconds()
unit == "b" ? f :
unit == "s" ? f / timeframe :
unit == "m" ? f*60 / timeframe :
unit == "h" ? f*60*60 / timeframe :
unit == "D" ? f*60*60*hid / timeframe :
unit == "W" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_week() / timeframe :
unit == "M" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_month() / timeframe :
unit == "Y" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_year() / timeframe : naおわりに
marginの値をより小さくするほど、より早く反応しますがダマしが多くなります。marginの計算を進化させてみてください。他にも、移動平均とのクロスをはじめとしたいろいろな方法でe1pの向きの判定ができると思います。お気に入りの方法を試してみてください。結果のレポートをお待ちしております。
上ではソースの注目部分のみを取り上げましたが、今回のEBBXのソース、使っているライブラリ dig_dig_11/lib_beta/1 の全体は次の通りです。
// This Pine Script™ code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © dig_dig_11
//@version=5
indicator("ebbx 202408", overlay=true)
import dig_dig_11/lib202408/1 as dd11
import dig_dig_11/lib_beta/1 as dd11b
var g_value = input.float(120, title="g value", minval=0, inline="g")
var g_unit = input.string("b", title="unit", options=["b", "s", "m", "h", "D", "W", "M", "Y"], inline="g",
tooltip="value\n"
+ " 次のunitとともに解釈される値\n"
+ "unit\n"
+ " b: bars\n s: seconds\n m: minutes\n h: hours\n D: days\n W: weeks\n M: months\n Y: years")
var exclude = input.int(5, title="exclude", minval=4, display=display.none,
tooltip="精度が低い最初のexclude*gで、塗りつぶしをしない")
var lic = input.string("", title="lic", display=display.none,
tooltip="入力なしで15分足まで使えます\n"
+ "より短い足で使うには https://x.com/dig_dig_11 のプロフィールから")
var extra_space = input.bool(not false, title="extra space", display=display.none,
tooltip="TradingViewのロゴが邪魔なときにチェックしてください")
// gを計算
var g = dd11b.readable2bars(g_value, g_unit)
// ebbx計算
[e0p, e0d, e1p] = dd11.ebbx(open, high, low, close, g, lic)
// バンド描画
var col_line = dd11b.gray(70)
plot(e0p + e0d*2, color=col_line, title="+2σ")
plot(e0p + e0d*1, color=col_line, title="+1σ")
plot(e0p - e0d*1, color=col_line, title="-1σ")
plot(e0p - e0d*2, color=col_line, title="-2σ")
// 塗りつぶし描画
var margin = dd11b.get_margin(g*timeframe.in_seconds()/60)
pos = dd11b.get_ebbx_pos(e1p, e0p, e0d, margin)
// pos = dd11b.get_ebbx_pos_simple(e1p, e0p) // simple_ebbx互換
col = dd11b.pos2col4(pos, not_enough=bar_index<g*exclude) // 4色版
// col = dd11b.pos2col3(pos, not_enough=bar_index<g*exclude) // 3色版
pe0p = plot(e0p, editable=false, display=display.none+display.price_scale, title="e0p")
pe1p = plot(e1p, editable=false, display=display.none+display.price_scale, title="e1p")
fill(pe0p, pe1p, color=col)
// 情報テーブル出力
var a_str = array.from(dd11b.second2readable(g*timeframe.in_seconds()), "")
var a_str_tt = array.from(str.tostring(g, "g=#.#bars ") + str.tostring(margin, "margin=#.0%"))
var tbl = dd11b.get_table(a_str, a_str_tt, columns=2, extra_space=extra_space)
if barstate.islast
tbl.cell_set_text(2, 0, text=str.tostring(e0d/syminfo.mintick, "#"))
for x = 1 to 2 // 0はextra spaceに使われている
tbl.cell_set_bgcolor(x, 0, dd11b.tune_color(col, transp=20))// This Pine Script™ code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © dig_dig_11
//@version=5
// @description dig_dig_11 beta library
library("lib_beta", overlay=true)
import dig_dig_11/lib202408/1 as dd11
///////
/////// number
///////
positive(float f) =>
dd11.positive(f)
negative(float f) =>
dd11.negative(f)
// @function より大きいか判定する
// @param f 判定される値
// @param g 基準の値
// @returns f > g の結果
export more_than(float f, float g) =>
positive(f - g)
// @function より小さいか判定する
// @param f 判定される値
// @param g 基準の値
// @returns f < g の結果
export less_than(float f, float g) =>
negative(f - g)
// @function 範囲内にクリップする
// @param i クリップされるint
// @param min クリップの下限
// @param max クリップの上限
// @returns クリップの結果
export clip(int i, int min, int max) =>
i < min ? min : max < i ? max : i
// @function 範囲内にクリップする
// @param f クリップされるfloat
// @param min クリップの下限
// @param max クリップの上限
// @returns クリップの結果
export clip(float f, float min, float max) =>
less_than(f, min) ? min : less_than(max, f) ? max : f
///////
/////// color
///////
color_at_phase(float phase, float min, float max) =>
p = phase % 360
val = less_than(p, 180) ?
min - (max-min)/60 * (p-120) : // p=120でminを通り、傾き-(max-min)/60
min + (max-min)/60 * (p-240) // p=240でminを通り、傾き(max-min)/60
clip(val, min, max)
// @function HSV色空間で指定された色を返す
// @param h 色相(hue) -60 <= h
// @param s 彩度(saturation) 0 <= s <= 100
// @param v 明度(value) 0 <= v <= 100
// @param t 透過度(transparency) 0 <= t <= 100
// @returns 指定された色
export hsv2color(float h, float s, float v, float t=0) =>
clipped_s = clip(s, 0, 100)
clipped_v = clip(v, 0, 100)
max = clipped_v/100 * 255
min = max * (1 - clipped_s/100)
color.rgb(color_at_phase(h, min, max), color_at_phase(h+240, min, max), color_at_phase(h+120, min, max), t)
// @function HSV色空間での成分を返す
// @param c 色
// @returns 入力された色のHSV色空間での成分
export color2hsv(color c) =>
rgb = array.from(color.r(c), color.g(c), color.b(c))
max_i = // 最大値のindex
more_than(rgb.get(0), rgb.get(1)) ? // 0、1どちらかを脱落させる
more_than(rgb.get(0), rgb.get(2)) ? 0 : 2 : // 1が脱落した後の処理
more_than(rgb.get(1), rgb.get(2)) ? 1 : 2 // 0が脱落した後の処理
fw_i = (max_i + 1) % 3 // forward index(max_iより位相が進んだindex)
bw_i = (max_i + 2) % 3 // backward index(max_iより位相が遅れたindex)
min_i = more_than(rgb.get(fw_i), rgb.get(bw_i)) ? bw_i : fw_i // 最小値のindex
h = rgb.get(max_i) == rgb.get(min_i) ? 0 : // 0除算防止
max_i * 120 // 0、120、240度の大枠決定
+ (rgb.get(fw_i) - rgb.get(bw_i)) / (rgb.get(max_i) - rgb.get(min_i)) * 60 // ±60度調整
s = rgb.get(max_i) == 0 ? 0 : // 0除算防止
(rgb.get(max_i) - rgb.get(min_i)) / rgb.get(max_i) * 100
[(h+360)%360, s, rgb.get(max_i)/255*100]
// @function 入力された色をHSV色空間で微調整する
// @param c 色
// @param tune_h hを調整する量 -360~360
// @param tune_s sを調整する量 -100~100
// @param tune_v vを調整する量 -100~100
// @param transp 透過度(調整量ではない) 0~100
// @returns 微調整された色
export tune_color(color c, float tune_h=0, float tune_s=0, float tune_v=0, float transp=na) =>
[h, s, v] = color2hsv(c)
h += tune_h + 360 // あまり何度もtune_color()を繰り返すと桁あふれすることがある
s += tune_s/100 * (negative(tune_s) ? s : 100-s)
v += tune_v/100 * (negative(tune_v) ? v : 100-v)
t = nz(transp, color.t(c)) // naの場合には元のtransp
hsv2color(h, s, v, t)
// よく使う色の定義
// tune_color()によるh、s、vの微調整、transpの指定も可能
export black(float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(0, 0, 0), transp=transp)
export white(float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(0, 0, 100), transp=transp)
export gray(float v=50, float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(0, 0, v), transp=transp)
export red(float tune_h=0, float tune_s=0, float tune_v=0, float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(0, 100, 92), tune_h, tune_s, tune_v, transp)
export green(float tune_h=0, float tune_s=0, float tune_v=0, float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(122, 100, 50), tune_h, tune_s, tune_v, transp)
export blue(float tune_h=0, float tune_s=0, float tune_v=0, float transp=na) => tune_color(hsv2color(215, 100, 90), tune_h, tune_s, tune_v, transp)
///////
/////// ebbx
///////
// @function e1pの方向の計算で使うmarginを計算する
// @param g_in_minutes 分単位で表したg
// @returns e0dに対する割合を表すmargin
export get_margin(float g_in_minutes) =>
// g_in_minutes=1のとき0.1(つまり10%)を返す
// g_in_minutes=256のとき0.05、256^2のとき0.025と、256倍になるたび0.5倍になる
0.1 * math.pow(0.5, math.log(g_in_minutes)/math.log(256))
// @function e1pの向きとe1pとe0pの上下関係でポジションを計算する
// @param e1p ebbxのe1p
// @param e0p ebbxのe0p
// @param e0d ebbxのe0d
// @param margin e1pの方向判定で、逆行を e0d*margin まで許す
// @returns ポジション(+2, +1, -1, -2)
export get_ebbx_pos(float e1p, float e0p, float e0d, float margin) =>
var dir = +1 // e1pの向き(+1 上向き、-1 下向き)
var h = e1p // e1pの直近高値
var l = e1p // e1pの直近安値
dir :=
less_than(e1p, h-e0d*margin) ? -1 : // 直近高値-e0d*marginをe1pが下回れば下向き
more_than(e1p, l+e0d*margin) ? +1 : // 直近安値+e0d*marginをe1pが上回れば上向き
dir
h := dir > 0 ? math.max(h, e1p) : e1p // 上向きのとき直近高値をmath.max(h, e1p)で更新
l := dir < 0 ? math.min(l, e1p) : e1p // 下向きのとき直近安値をmath.min(l, e1p)で更新
dir > 0 ? // dirが正なら強気
more_than(e1p, e0p) ? +2 : +1 : // e1p > e0pだとより強気
less_than(e1p, e0p) ? -2 : -1 // e1p < e0pだとより弱気
// @function e1pの傾きとe1pとe0pの上下関係でポジションを計算する
// @param e1p ebbxのe1p
// @param e0p ebbxのe0p
// @returns ポジション(+2, +1, -1, -2)
export get_ebbx_pos_simple(float e1p, float e0p) =>
less_than(e1p[1], e1p) ? // e1pが右上がりなら強気
more_than(e1p, e0p) ? +2 : +1 : // e1p > e0pだとより強気
less_than(e1p, e0p) ? -2 : -1 // e1p < e0pだとより弱気
///////
/////// pos2col
///////
// @function ポジションで4色に塗り分ける
// @param pos ポジション
// @param not_enough 経過時間が短いので色分けしない
// @param color_bull0 弱買の色
// @param color_bull1 買の色
// @param color_bear0 弱売の色
// @param color_bear1 売の色
// @returns 選択された色
export pos2col4(int pos, bool not_enough=false, color color_bull0=na, color color_bull1=na, color color_bear0=na, color color_bear1=na) =>
var col_bull0 = nz(color_bull0, red(tune_s=-80, tune_v=+100)) // 弱買
var col_bull1 = nz(color_bull1, red(tune_s=-50, tune_v=+70)) // 買
var col_bear0 = nz(color_bear0, blue(tune_s=-80, tune_v=+100)) // 弱売
var col_bear1 = nz(color_bear1, blue(tune_s=-50, tune_v=+70)) // 売
not_enough ? na :
pos > 0 ? pos > 1 ? col_bull1 : col_bull0 :
pos < 0 ? pos < -1 ? col_bear1 : col_bear0 :
na // pos == 0 のとき
// @function ポジションで3色に塗り分ける
// @param pos ポジション
// @param not_enough 経過時間が短いので色分けしない
// @param color_bull 買の色
// @param color_bear 売の色
// @param color_neutral 中立の色
// @returns 選択された色
export pos2col3(int pos, bool not_enough=false, color color_bull=na, color color_bear=na, color color_neutral=na) =>
var col_bull = nz(color_bull, red(tune_s=-60, tune_v=+80)) // 買
var col_bear = nz(color_bear, blue(tune_s=-60, tune_v=+80)) // 売
var col_neutral = nz(color_neutral, gray(85)) // 中立
not_enough ? na :
pos > 1 ? col_bull :
pos < -1 ? col_bear :
col_neutral // -1 <= pos <= 1 のとき
///////
/////// tool
///////
// @function 指定されたテーブルを作る
// @param a_str テーブルに表示する文字列の配列。横優先で入れる。データがなくても""などを入れる
// @param a_str_tt ツールチップで表示する文字列の配列。横優先で入れる
// @param columns テーブルの幅(extra_spaceは含まない)
// @param position テーブルの表示位置 position.top_left, position.top_center, position.top_right, position.middle_left, position.middle_center, position.middle_right, position.bottom_left, position.bottom_center, position.bottom_right
// @param bgcolor 背景色
// @param text_color 文字列の色
// @param text_size 文字列の大きさ size.auto, size.tiny, size.small, size.normal, size.large, size.huge
// @param text_halign 横方向の配置方法 text.align_left, text.align_center, text.align_right
// @param extra_space 左に場所を空けるかどうか
// @returns 生成されたテーブル
export get_table(array<string> a_str, array<string> a_str_tt=na, int columns=1,
string position=position.bottom_left,
color bgcolor=na,
color text_color=na,
string text_size=size.normal,
string text_halign=text.align_right,
bool extra_space=false) =>
var col = nz(text_color, black())
var col_bg = nz(bgcolor, gray(95))
var count = array.size(a_str)
var count_tt = na(a_str_tt) ? 0 : array.size(a_str_tt)
var rows = count / columns
var tbl = table.new(position, 1+columns, rows) // カラム0はextra_space用に追加
if extra_space
tbl.cell(0, 0, text=" ", text_size=size.small) // 場所を空けるため
for y = 0 to rows-1
for x = 0 to columns-1 // 横優先で入っているので、内側ループでは横を連続して処理
index = y*columns + x
if index < count
tbl.cell(1+x, y, text=array.get(a_str, index), text_size=text_size, text_halign=text_halign, text_color=col, bgcolor=col_bg)
if index < count_tt
tbl.cell_set_tooltip(1+x, y, array.get(a_str_tt, index))
tbl
///////
/////// time
///////
// 週7日動いている市場などでは変えたほうがよい
get_hours_in_day() => 24
get_days_in_week() => 5
get_days_in_month() => 21
get_days_in_year() => 259
// @function 値と単位からbarの数に換算する
// @param f 値
// @param unit 単位
// @returns 換算されたbarの数
export readable2bars(float f, string unit) =>
var hid = get_hours_in_day()
var timeframe = timeframe.in_seconds()
unit == "b" ? f :
unit == "s" ? f / timeframe :
unit == "m" ? f*60 / timeframe :
unit == "h" ? f*60*60 / timeframe :
unit == "D" ? f*60*60*hid / timeframe :
unit == "W" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_week() / timeframe :
unit == "M" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_month() / timeframe :
unit == "Y" ? f*60*60*hid*get_days_in_year() / timeframe : na
// @function 秒を読みやすい単位に換算にする
// @param s 秒で表された時間
// @returns 読みやすい単位に換算した結果
export second2readable(float s) =>
var hid = get_hours_in_day()
s < 60 ? str.tostring(s, '#s') :
s < 60*60 ? str.tostring(s/60, '#m') :
s < 60*60*hid ? str.tostring(s/60/60, '#.#h') :
s < 60*60*hid*get_days_in_week() ? str.tostring(s/60/60/hid, '#.#D') :
s < 60*60*hid*get_days_in_month() ? str.tostring(s/60/60/hid/get_days_in_week(), '#.#W') :
s < 60*60*hid*get_days_in_year() ? str.tostring(s/60/60/hid/get_days_in_month(), '#.#M') :
str.tostring(s/60/60/hid/get_days_in_year(), '#.#Y')ここから先は
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
