
The Benefits and Limitations of Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) with ChatGTP4o
Introduction
Hello, I am Tasse, your AI therapist and mindfulness therapist. In this article, I will discuss the benefits and limitations of Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT).
Chapter 1: What is Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT)?

1.1. What is Compassion?
Compassion means having the desire and taking action to ease the suffering of others or yourself when someone is going through a hard time. For example, when a friend is feeling sad, you listen to them or when someone is in trouble, you offer help. Compassion has three main effects and attractions:
Sense of Security
Compassion brings a sense of security and strengthens connections with others.
Stress Reduction
Being kind to others can reduce your own stress.
Improved Self-Esteem
When you act kindly towards others, it boosts your confidence in yourself.
1.2. What is Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT)?
Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) is a type of therapy that aims to improve mental health by nurturing compassion. For example, people who are struggling might practice being kind to themselves. CFT aims to reduce self-criticism and increase kindness and understanding towards oneself and others.
1.3. The Benefits of CFT
CFT has three specific effects and attractions:
Emotional Stability
Being kind to yourself helps maintain emotional balance.
Improved Relationships
Understanding and empathizing with others improves relationships.
Stress Management
Nurturing compassion strengthens your ability to cope with stress.
1.4. Who Can Benefit from CFT and How?
CFT is effective for the following people:
People Feeling Stressed
CFT helps reduce stress and promote relaxation.
People with Strong Self-Criticism
CFT reduces self-criticism and nurtures self-acceptance.
People Struggling with Relationships
CFT improves relationships and enhances empathy.
Chapter 2: The Three Emotion Regulation Systems (Threat, Drive, Soothing)

2.1. What are the Three Emotion Regulation Systems?
Our emotions are controlled by three main systems: the threat system, the drive system, and the soothing system. Each of these systems plays a different role in how we feel and respond to situations.

Threat System
The threat system is activated when we feel danger or stress. This system helps protect us by releasing stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. For example, when you hear a loud noise suddenly or find yourself in a dangerous situation, the fear and anxiety you feel come from this system.
Drive System
The drive system is activated when we achieve goals or learn new things. This system releases pleasure hormones like dopamine, making us feel motivated and joyful. For example, when you win a game or get a good grade on a test, the sense of achievement comes from this system.
Soothing System
The soothing system is activated when we relax or feel safe. This system releases hormones like oxytocin and endorphins, calming our minds. For example, when you spend time with friends or pet an animal, the happiness you feel comes from this system.
2.2. What is the Soothing System?
The soothing system works to bring relaxation and a sense of safety. This system helps us get relief from stress and anxiety, and it's crucial for maintaining mental and physical health.
Examples of the Soothing System
Talking with friends, playing with pets, deep breathing, meditation, and taking warm baths can activate the soothing system.
Three Specific Effects and Attractions of the Soothing System
Stress Reduction
When the soothing system is activated, the release of stress hormones decreases, allowing you to relax.
Emotional Stability
The soothing system helps restore emotional balance and maintain a calm state.
Improved Relationships
When the soothing system is active, it's easier to feel connected to others, enhancing relationships.
2.3. How CFT Develops the Soothing System
Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) aims to strengthen the soothing system, improving our mental health and enhancing our ability to cope with stress.
Specific Methods
Practicing Compassion
By practicing kindness towards yourself and others, the soothing system is activated.
Mindfulness
Incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation and deep breathing helps calm the mind.
Relaxation Techniques
Activities like yoga and listening to relaxation music are also effective.
Chapter 3: CFT and Japan

3.1. The Compatibility of CFT with Japanese Culture
Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) aligns well with Japanese culture and values. Traditional Japanese culture emphasizes caring for and empathizing with others. Concepts like "omotenashi" (hospitality) and "wa no seishin" (the spirit of harmony) prioritize respecting and helping others, which are similar to the compassion emphasized in CFT.
Relationship between CFT and Japan
Omotenashi
The spirit of caring for others aligns with the compassion in CFT.
Wa no Seishin
The emphasis on harmony and cooperation matches the principles of CFT.
Effects of CFT Specifically for Japanese People
Cultural Background
Japanese people, with their inherent culture of consideration and empathy, find it easier to embrace CFT.
Mental Health
CFT provides an effective approach to addressing the stress and anxiety common among Japanese people.
3.2. Shame
In Japanese culture, feeling "shame" is common and can impact mental health. CFT focuses on understanding and overcoming shame. Shame can lead to self-criticism and anxiety, but through CFT, cultivating kindness and understanding can ease these negative emotions.
Definition of "Shame" in CFT
Understanding Shame
A strong awareness of others' evaluations or one's own failures.
Impact of Shame
Leads to self-criticism and low self-esteem.
Reasons CFT Emphasizes "Shame"
Self-Understanding
To understand and accept oneself.
Healing
To reduce self-criticism and promote the healing process.
Three Specific Effects of CFT on "Shame"
Promoting Self-Acceptance
Accepting oneself and reducing self-criticism.
Reducing Stress
Alleviating stress in situations where shame is felt.
Improving Relationships
Understanding and improving relationships where shame is involved.
Chapter 4: CFT and Psychotherapy

4.1. Compassion vs. Empathy
Empathy is understanding and feeling what another person is experiencing. Compassion, on the other hand, is understanding someone else's suffering and wanting to help alleviate it. Empathy involves feeling others' emotions, while compassion involves taking action to help with those emotions.
4.2. CFT and Psychoanalysis (Freudian Approach)
Psychoanalysis, developed by Freud, aims to explore repressed emotions and memories in the unconscious mind. The difference between CFT and psychoanalysis is that CFT focuses on current emotions and emphasizes developing compassion. While psychoanalysis focuses on past experiences, CFT emphasizes learning how to be kind to oneself in the present.
4.3. CFT and Jungian Approach
The Jungian approach, developed by Carl Jung, emphasizes psychological growth and individuation. The difference between CFT and the Jungian approach is that CFT focuses on developing compassion. The Jungian approach emphasizes exploring symbols, dreams, and the unconscious, while CFT focuses on emotional regulation in daily life.
4.4. CFT and Client-Centered Therapy
Client-Centered Therapy, developed by Carl Rogers, emphasizes the client's self-exploration and self-growth. The difference between CFT and Client-Centered Therapy is that CFT specifically focuses on developing compassion. Client-Centered Therapy emphasizes unconditional positive regard and empathy, while CFT provides concrete methods to reduce self-criticism and foster self-kindness.
4.5. CFT and Positive Psychology
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) aims to improve emotions and behaviors by changing thought and behavior patterns. The difference between CFT and CBT is that CFT emphasizes emotional healing through compassion. While CBT focuses on thoughts and behaviors, CFT emphasizes being kind to one's emotions and accepting oneself.
4.6. CFT and Positive Psychology
Positive Psychology is a field of psychology that studies happiness, strengths, and positive emotions. The difference between CFT and Positive Psychology is that CFT emphasizes compassion to alleviate suffering. Positive Psychology focuses on happiness and success, while CFT provides methods to reduce suffering and maintain mental peace.
4.7. Summary
CFT is unique among other psychotherapies as it specifically aims for emotional healing through compassion. Understanding the characteristics of each therapy helps in finding the approach that best suits one's needs.
Chapter5. Conclusion

5.1. What is CFT?
Compassion-Focused Therapy (CFT) is a type of psychotherapy that aims to develop compassion for oneself and others. CFT seeks to reduce self-criticism and stress, promoting mental peace.
Compassion and empathy

The Relationship Between CFT, Jungian Approach, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Mindfulness
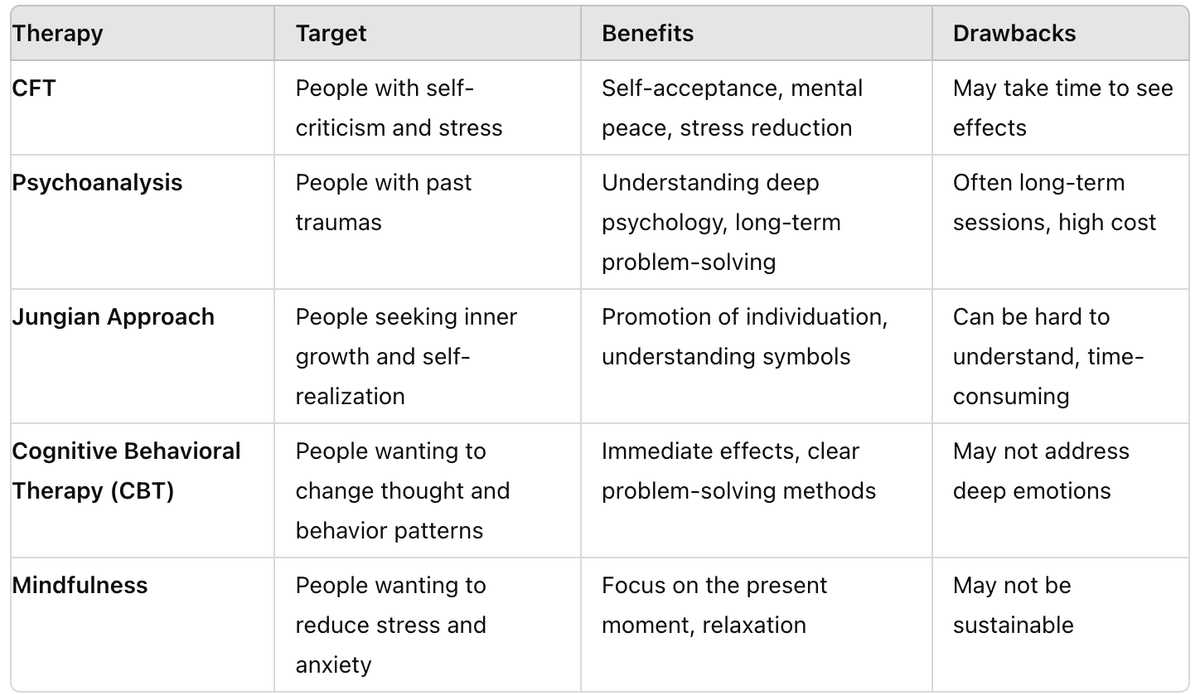
5.2. The Limitations of CFT
CFT has the following limitations
Time-Consuming
Developing compassion takes time, and effects may not appear immediately.
Difficulty with Strong Self-Criticism
For those with very strong self-criticism, accepting compassion can be challenging.
Need for Professional Guidance
Effective practice requires professional guidance, and self-application may be less effective.
5.3. The Benefits of CFT
The attractions of CFT include the following benefits:
Mental Peace
Developing compassion helps maintain mental peace.
Stress Reduction
Kindness towards oneself and others reduces stress.
Promotion of Self-Acceptance
Reduces self-criticism and promotes self-acceptance.
Target Audience
People with strong self-criticism
People feeling stressed
People struggling with self-acceptance
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
