
Smart Bus Stop System
Prologue
G7 Digital Ministerial Meeting Held in the Regional City of Takasaki, Japan
The recent G7 Digital Ministerial Meeting was held at G-Messe Gunma, located in Takasaki City, Gunma Prefecture im Japan. This convention facility, the first of its kind in Gunma, opened at the same time as the COVID-19 pandemic began to spread. Initially, it was said to be unprofitably, however, circumstances have turned out quite differently.
Recently, as the COVID-19 situation has finally started to calm down, domestic and international companies involved in digital technology gathered at the convention venue in parallel with the Digital Ministerial Meeting. The fact that the event took place in Gunma Prefecture, and the convention being held there, evoked a deep sense of significance. One of the reasons for choosing this location for the G7 conference seems to be the convenience of public transportation.
Indeed, Takasaki City has been a major transportation hub for a long time, approximately one hour from Tokyo Station by Shinkansen. It has been an important junction along the Nakasendo, an ancient highway. However, it should be noted that the convenience of transportation is limited to the city center and the areas surrounding Takasaki Station, focusing mainly on the JR mainlines. Like other regional cities, if one wish to go travel even a little farther away, using a car becomes essential due to the lack of regional public transportation other than trains and buses.
Challenges of Regional Public Transportation
While I mentioned "Takasaki City" specifically, it is not unique to Takasaki however, applies to all of Gunma Prefecture. For example, Maebashi, the prefectural capital, is not along major railway lines. Therefore, both travel to Tokyo and regional mobility are hindered. On the other hand, the Jomo Electric Railway, which plays a role in regional transportation in another area of the JR Ryomo Line, struggles to maximize its potential and due to management issues that make it difficult tu procure new vehicles due to aging and replacement concerns. One of the reason is the terminal station, Chuo-Maebashi station, is located far from JR Maebashi Station, and changing train is unfeasible. This is a common challenge faced by railway operations in regional cities, not only in Gunma Prefecture.
Bus services, which are responsible for regional public transportation like trains, also facing financial difficulties. Unlike railways, buses do not require the maintenance costs of infrastructure like tracks since they operate on roads. However, they have a larger number of routes and bus stops due to their ability to provide flexible and detailed transportation services. Limited numbers of vehicles and drivers, as well as delays caused by traffic congestion, affect to the frequency of bus services relatively low. This becomes one of the reasons for decline the users. Additionally, in the same region, multiple bus operators often operate independently with their own schedules and fares. This situation of multiple bus stop signs in one location, deviates from the concept of regional public transportation and hinders "convenience."
The reality is that various issues exist within regional bus services not only in Gunma Prefecture but also throughout regional cities nationwide. However, some cities, such as Kumamoto, Okayama, and Maebashi, have initiated efforts to unify bus operations among multiple operators to streamline regional bus services. This is driven by a sense of crisis shared by both local administrations and operators, Recognizing the importance of the decline of public transportation, which is increasingly crucial as Japan's society faces an aging population. Such initiatives should be closely observed as they serve as noteworthy examples. It is undeniable that achieving better regional public transportation is essential and indispensable for advancing community development.
The Future of Bus Stops
Many bus stops have remained unchanged since the Showa era, reflecting the fact that despite being an essential infrastructure for public transportation, bus operations are forced to be financially independent. Most bus stop signs are not installed in the ground, except in large cities such as Tokyo, and most of them are stand-alone structures with a cost of around tens of thousands Japanese yen per unit. With bus operators already struggling to manage their businesses, investing in vehicle maintenance, procuring new buses, and employment of drivers are essential investments, making it difficult to allocate funds for other improvements. However, we must not forget what is important for the users, and that is the fact that bus stops are "the most accessible gateway for transportation" for residents in local area. In this age, IT based innovative products is transforming society bus stops that remain stuck in a decades-old situation will further decrease the number of users and lead to an inefficient transportation system, wasting the efforts made to improve the most accessible form of public transportation. Paradoxically, if bus system is designed to be user-friendly, providing convenient and stress-free transportation from the users' perspective, it can be expected to be welcomed by the local residents and visitors.
The Ideal Bus Stop
So, what would be the ideal bus stop for both users and operators? The key is to ensure that the following information is accurately conveyed to the users for maximum convenience:
Bus stop name
Destination and route number
Departure time of the bus to be boarded
Delay information (estimated delay time)
Timetable and route map
Current time
In addition to the above, it is essential for the bus stop to have a visible presence that asserts its identity as a bus stop and can be recognized from a distance. Safety is also essential, ensuring that it remains upright even in strong winds or due to human interference. Furthermore, if the bus stop incorporates technology to provide real-time bus operation information through the mobile phone applications and allows for pre-payment of fares, it would be more compatible with Mobility as a Service (MaaS) initiatives.
Creating Profitable Bus Stops
It is clear that the cost of implementing the above-mentioned bus stops would be significantly higher than the current situation. Given the financial difficulties faced by most local bus operators, it is extremely difficult for them to allocate funds for such improvements. However, if the bus stops themselves can generate revenue, they could cover the maintenance costs, as well as the initial installation expenses. Although implementing and operating such bus stops is necessary to generate revenue, one possible approach to overcome the cost barrier is to engage in lease agreements with local banks, which would also fulfill their mission of contributing to the local community.
The Concept of Self-Sustaining Bus Stops

Recently, it has become common to see roofed bus stops with large advertisements displayed, particularly in large cities such as Tokyo. This is a business model implemented by bus stop specialized company in France and elsewhere, where they generate revenue from advertising without burden on the bus operators. They take care of everything from the installation to their maintenance. These roofed bus stops have begun to appear in regional cities such as Takasaki and Maebashi. However, these roofed bus stops require space on the sidewalk, and physically installing on relatively wide sidewalks in such as city centers. The advertisements of these bus stops consist of one large advertisement on the front and back sides of the space, which is regularly replaced. The advertisements are in paper, and the operational information provided is also analogue timetable in analog format. However, these bus stops can generate income through advertising. Moreover, since they have all the same design, they lack a strong identity as bus stops, and there are many points that need to be improved.
Bus stop with enhanced convenience

Another type of bus stop displays operational information in digital signage in real-time which has developed by a domestic manufacturer. They incorporate small digital signage screens into conventional bus stops, which display information about the destination, route number, and departure times of the buses stopping with scrolling. This provides real-time information for the next bus arrivals, making it a more convenient product compared to conventional bus stops. However, these smart bus stops and signage advertising need fare revenue from large number of the user or adequate budget. Additionally, these bus stops cannot accrue profit. Therefore, maintaining bus stops is financially challenging for many operators in regional cities. Furthermore, the design and structure of the bus stop itself has not significantly changed from the conventional design, so there are still problems regarding the presence and identity of the bus stop.
The Ideal Bus Stop: Beneficial for Users and Operators
We have considered the advantages and disadvantages of the two types of current bus stops mentioned above. The primary goal is to realize the ideal bus stop for regional cities. To achieve this, following requirements should be fulfilled.
The bus stop required to generate its own revenue to cover installation and maintenance costs.
It should provide high convenience by displaying real-time bus operational information.
The design of the bus stop structure should enhance visibility and have a strong presence.
It should integrate with mobile phone applications pushing information and support Mobility as a Service (MaaS) initiatives.
Proposal for Self-Sustaining Smart Bus Stop
Research and Analysis

Currently, most bus stops in rural areas face various problems. For example, they may be too small and difficult to find, several bus stops placed haphazardly, or placed at a distance. When bus stops, with lack information, are located, first-time users often feel uncertain their desired bus route will stop there. There have been unfortunate incidents where bus stops were intentionally knocked down for safety during approaching typhoons. All these issues stem from insufficient funding, despite public transportation being a lifeline for citizens.
Concept
Self-Sustaining Smart Bus Stop System
Utilizing AI-based IoT technology for bus stops is an effective solution to address the current problems. The proposed system includes the following features:
Positioning the bus stops as "the gateway to local transportation."
Graphic and product design that effectively conveys the message of "presence of a bus stop."
Integration with mobile phone application (MaaS) for providing real-time operational information (payment function will be integrated in future).
Delivery of "advertising and public relations media" through both bus stop signage and the mobile phone application, covering three domains: "businesses general operators," "local operators," and "governmental promotion."
Achieving a completely new smart bus stop that maximizes business and social contributions through AI-optimized ad scheduling and pricing, resulting in a vast number of deliveries and revenue maximization.

Design (form and symbolization)
A form that visually impresses "STOP", which respects the German semaphore railway signal. A bus stop design that is noticeable by the users and bus drivers. This symbol mark will appeal the bus stop effectively.

Digital signage with operational information
Display of operational information (Passenger Information System) in approximately one-fourth of the signage's upper space.
Real-time display of current time, departure time, route number, destination, and remaining time until departure (in minutes) for two buses, scrolling operational information.
Approximately three-fourths of the signage's lower space dedicated to advertising.
Three Types of Signage Advertising

Advertisements posted on signage are categorized into three types (general advertisements, local advertisements, administrative advertisements), and the following contents are delivered.
General Advertisement: Advertisement mainly for large companies nationwide
Local advertisement: Advertising for local shops, clinics, sole proprietors, etc.
Advertisement: Guidance from the government, disaster information, local events, one-line announcements from the general public (e.g. looking for a lost dog), etc.
General advertising is handled by advertising agencies, local advertising by regional chambers of commerce, and one-line government announcements (free of charge) through the municipal office as the contact point. Inputting information is possible via PC or mobile phone application, which is centralized on a server, organized, and distributed after undergoing a review for public order and morality (allowing image and video file uploads, selection of delivery stops and desired time slots, and including payment functionality).
Revenue Simulation

Signage advertising operation setting is as follows,
Advertising delivery time: 0:00 to 24:00 (24 hours/day)
Delivery time per advertisement: 15 seconds (static images, videos)
Category-based delivery time per hour: Up to 25 minutes for general advertising, up to 25 minutes for local advertising, and a minimum of 10 minutes for government announcements
Flexible pricing is set for three fare categories: regular operating hours, peak commuting hours, and non-operating hours. Collected data, for example, number of the passenger per hour, will be used for learning AI and dynamically updates the price in each bus stop; to optimize the revenue.
The advertising cost per bus stop (two units) is calculated at JPY 10 per minute (4 advertisements of 15 seconds each), estimated income will be JPY 12,000 per day and JPY 4,380,000 per year (the pricing is referred from the advertising fee at a post office signage).
Electronic advertising at bus stop by time slot sale can reduce the advertising price compare than print advertising and make it affordable for the advertiser.
It is not only encourages the excavation of latent demand in the region and strengthens the advertising competitiveness of well-known general companies but also contributes to the provision of citizen services by securing time slots for administrative announcements;. For example, an emergency notifications, an announcements for local facilities such as community centers and a public schools, event announcements by the administration and a NPO/NGOs, and brief notices by citizens will be displayed free of charge. This allows for the realization of not only profitability but also the social mission through smart bus stops.
In cases where the advertising time falls below the expected number of slots, administrative announcements displays supplementary.
Furthermore, in addition to the information displayed on the signage, the same content is delivered through dedicated tablet and smartphone apps. By scanning the QR code at each bus stop, users, whether they possess a smartphone or not, can access the same information available on the signage through the app. This functionality enables everyone, regardless of smartphone ownership, to access all the information related to the bus stop through the smart bus stop itself.
Lineup
The lineup of smart bus stops consists of four types. Type A "POLE;" is a main model. It is single-leg, installed-in-ground design. Additionally, there are another two types;. Type B "ELIPSE," which is for multiple lines bus stops, such as at the bus terminal in front of a station. Type C "ROOF," which incorporates "ELIPSE" into the bus stop with a roof and a windbreaker. All types are designed based on same concept and can offer flexible lineup to adapt the required environment.
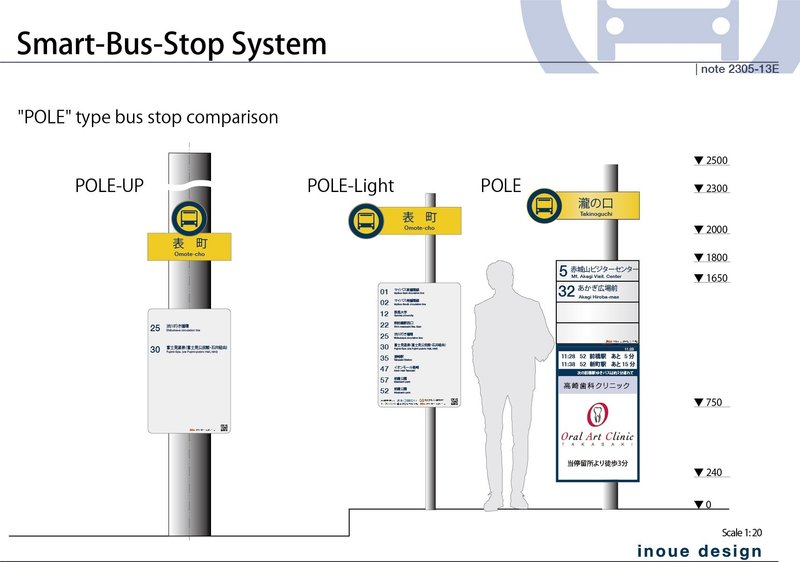
Type A: POLE

The standard type is designed to accommodate various bus stop environments. It features a single raised pole with the bus stop name and symbol mark at the top. Upper section of free layout modular panels displaying route numbers, destinations, and operating companies. The lower section includes vertical signage for real-time operational information and advertising. Timetables and other information are placed on the backside of the signage. Depending on the road environment and the number of users, without signage is also available. Since each part follows a modular structure, signage can be added later if needed. While the "POLE" without signage doesn't generate advertising revenue for the bus stop itself, this business model consider the overall system revenue per route. However, by scanning the QR code displayed at the bus stop, the user can access operational information and advertisements same as other smart bus stops through the mobile phone application. (Price verification of advertising revenue by the mobile phone application will be estimated later.)
Type B: ELIPSE
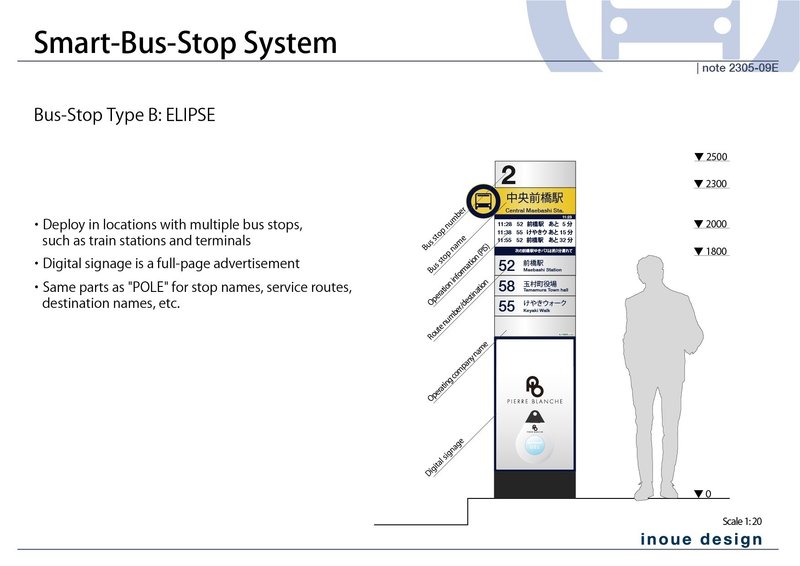
Type B "ELIPSE" is a one of the variations for bus terminals which covers multiple buse lines, such as in front of a station. It is named after elliptical cross-section of the bus stop body. The number at the top represents the bus stop number. Separate display of signage advertisements is available. (Pricing for each unit is dynamically determined by AI.)
Type C: ROOF

Type C "ROOF" incorporates "ELIPSE" into existing covered bus stops. While sharing the same design concept as "POLE," modular structure, allows to optimal variations which based on the usage environment, such as replacing the operational information display with different signage.
POLE-Light: Simplified POLE
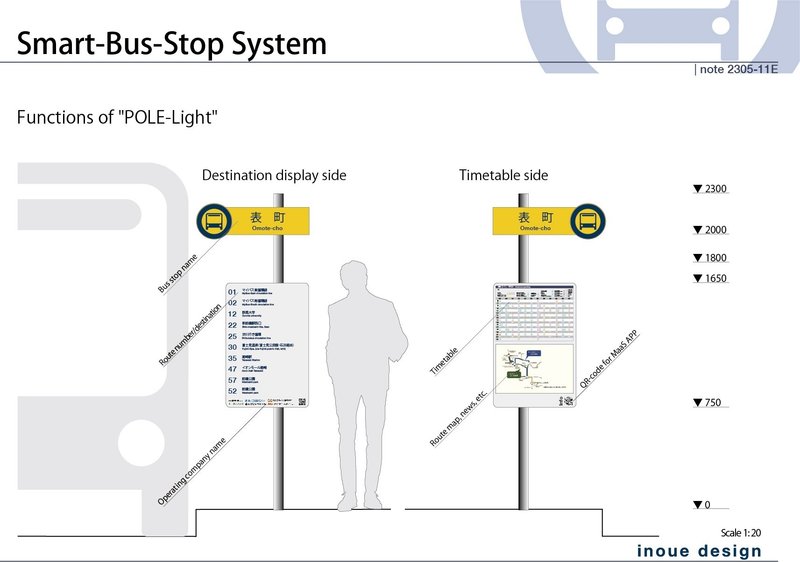
"POLE-Light" is a simplified version of "POLE" without signage, aiming to reduce installation costs. It retains the design concept of "POLE" but provides only essential information. The top section of the flat panel displays bus stop symbol and name of bus stop. At the bottom section indicates the route numbers, the destinations, the operating bus company, and on the opposite side, there are timetables and route maps. QR code for mobile phone application is also attached. Through the mobile phone application, the user can access the bus stop information as the one with the signage. The information in the bottom part is covered and secured with screw-fixed acrylic plate, ensuring the aesthetic appearance while preventing theft and dirt. Although it is a simplified version, it meets the same safety standards as the standard embedded bus stop.
POLE-UP: Narrow Road Type
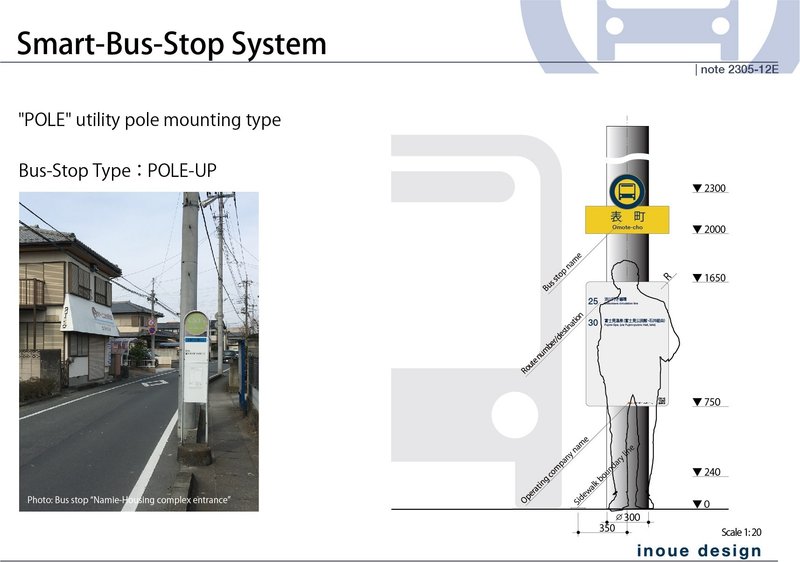
Special applications, the "POLE-UP" type is designed to be mounted on utility poles for narrow roads where there is no space (sidewalks) to install the bus stop unit. It resembles "POLE" while incorporating a design that prevents contact accidents. Although it does not have signage, the user can obtain operational information same as other smart bus stops by scanning the QR code.
Display Structure and network Diagramm
The Structure of the POLE

The signage attached to the smart bus stops is equipped with a 42-inch display screen. To prevent theft and damage, the screen is covered with anti-reflective reinforced glass and a metal frame.
Internet-connected Smart Bus Stops

All smart bus stops, regardless of the presence of signage, are connected to the internet, allowing access to all bus stop-related information even if the user is not near the bus stop. By scanning the QR code posted at the bus stop, the user can directly access the operational information, advertisements, and other relevant content displayed.
Smart Bus Stops Network Diagram
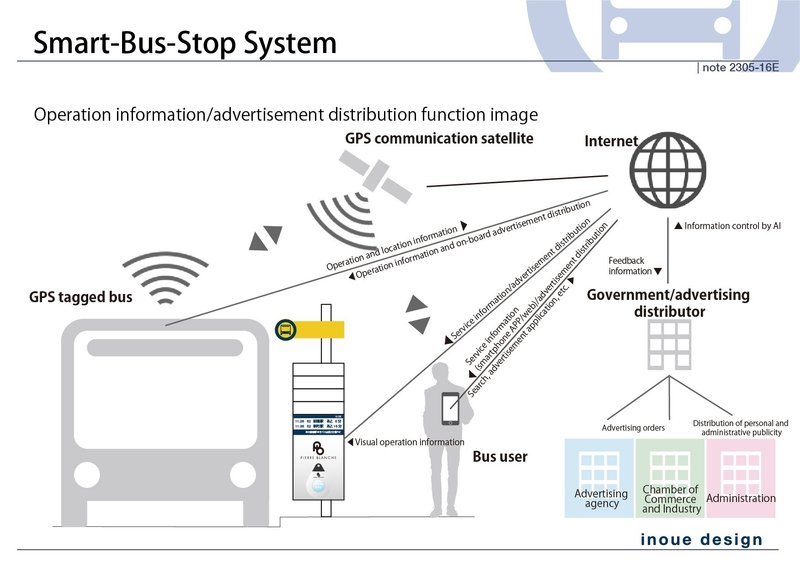
Smart bus stops serve as crucial access points for the entire system, delivering and displaying bus location information, schedules, delays, congestion, operational guidance, announcements, advertisements, and government notices through the signage via the internet. The information gathered from sensors, such as the number of users, is sent to servers and utilized for learning AI as big data, enabling the assessment of congestion and dynamic pricing for advertisements. (Smart bus stops can also provide Wi-Fi connection.)
Users can access to the operational information, advertisements, and all publicly available information related to bus services by using their mobile phones. Furthermore, by leveraging historical data, such as usage points, it becomes possible to promote the operators' services and provide payment functions that align with the advancement of Mobility as a Service (MaaS).
There are three different ways for advertising applications, depending on the respective positions, but all input processes can be entered through a PC or mobile phone applications. (For public announcements by the local government, applications can also be submitted at the municipal office.)
Epilogue
The city of Takasaki, where the G7 Digital Ministerial Meeting took place, is a typical regional city, as mentioned at the beginning. Although the city has excellent public transportation, guaranteeing fast and comfortable access to the city center through the Shinkansen and other means, when considering transportation from JR Takasaki Station to homes and other destinations, it is almost impossible to rely on anything other than cars. This situation is not only in Takasaki but also in many regional cities nationwide. Therefore, a fundamental reform of public transportation by buses, along with the corresponding improvement of bus stop facilities, is essential. Paradoxically, by accomplishing this, the current inconveniences associated with buses can transform into a convenient means of transportation that caters to people's lifestyles with richness and minimal stress.
In recent years, time have changed dramatically, and during this period, the reform of bus stops, which has remained unchanged since the Showa period in Japanese calemdar, will greatly change the perception. It will lead to a more prosperous and stress-free way of life for citizens, administrations, businesses, and communities.
Finally...
The Smart Bus Stop System project is currently ongoing and aims to continue evolving. I will update this article according to the progress of the project. If you have read this article and are interested in learning more or wish to contribute to practical application, we welcome contact from companies, educational and research institutions, operators, and those involved in administration.
Copyright 2023 inoue design All rights reserved
"The content and design of this article were created by me (inoue design) and the intellectual property rights belong to me. Unauthorized reproduction, modification, or commercial use is strictly prohibited, and legal action may be taken against any violations."
inoue design | Akira Inoue
Contact:
この記事が気に入ったらサポートをしてみませんか?
